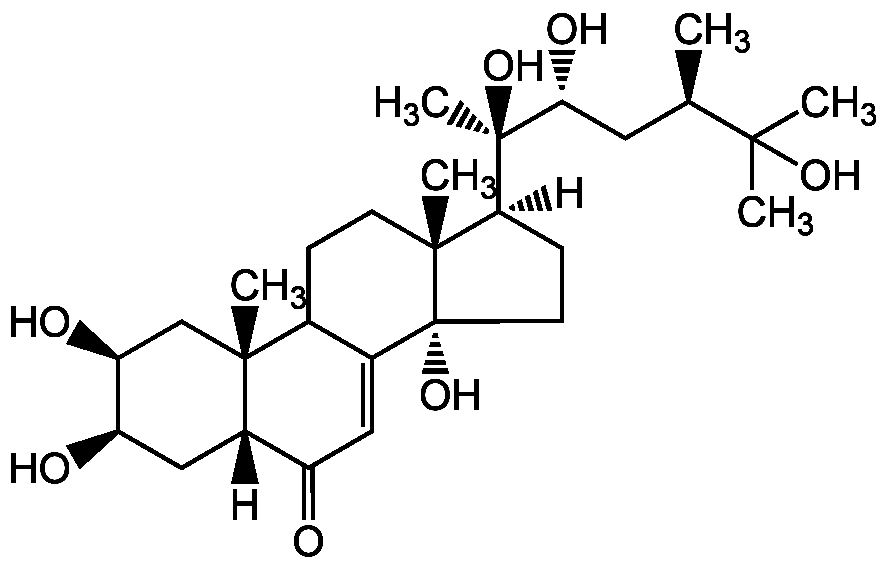
Chemical Structure
Makisterone A
AG-CN2-0073
CAS Number20137-14-8
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight494.7
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameMakisterone A
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number20137-14-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC28H46O7
- Molecular Weight494.7
- Scientific DescriptionA member of the ecdysteroid family. Ecdysone receptor (EcR) agonist. Induces the expression of genes coding for proteins that the larva requires, and it causes chromosome puffs (sites of high expression) to form in polytene chromosomes. Plays a role in insect development, cell proliferaton, growth and apoptosis by controlling gene expression involved in moulting and metamorphosis. It acts through a heterodimeric receptor comprising the ecdysone receptor and the ultraspiracle proteins (USP). Appears in plants mostly as a protection agent (toxins or antifeedants) against herbivorous insects. Could be used for controlled gene expression in scientific research, agriculture and medicine. Could be used for the development of selective insect growth regulators for use as environmentally benign insecticides. - Chemical. CAS: 20137-14-8. Formula: C28H46O7. MW: 494.7. Isolated from Ipomoea hederacea. A member of the ecdysteroid family. Ecdysone receptor (EcR) agonist. Induces the expression of genes coding for proteins that the larva requires, and it causes chromosome puffs (sites of high expression) to form in polytene chromosomes. Plays a role in insect development, cell proliferaton, growth and apoptosis by controlling gene expression involved in moulting and metamorphosis. It acts through a heterodimeric receptor comprising the ecdysone receptor and the ultraspiracle proteins (USP). Appears in plants mostly as a protection agent (toxins or antifeedants) against herbivorous insects. Could be used for controlled gene expression in scientific research, agriculture and medicine. Could be used for the development of selective insect growth regulators for use as environmentally benign insecticides.
- SMILES[H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2(O)C3=CC(=O)[C@]4([H])C[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)C[C@]4(C)C3CC[C@]12C)[C@@](C)(O)[C@H](O)C[C@@H](C)C(C)(C)O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Makisterone A [20137-14-8]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/5C/CgoaEGY7MOeEWB3BAAAAAO1PaRo754.png)