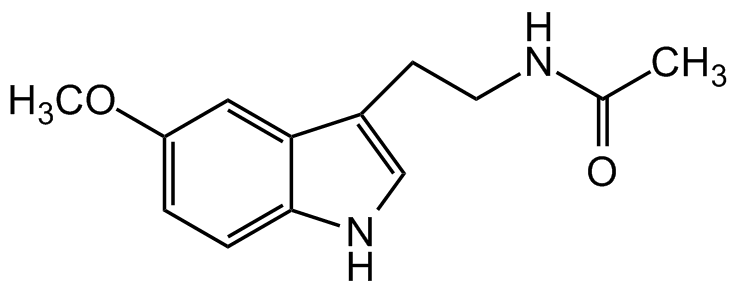
Chemical Structure
Melatonin [73-31-4] [73-31-4]
CDX-M0466
CAS Number73-31-4
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight232.28
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameMelatonin [73-31-4] [73-31-4]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number73-31-4
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC13H16N2O2
- Molecular Weight232.28
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 73-31-4. Formula: C13H16N2O2. MW: 232.28. Melatonin is an endogeneous hormone that plays a prominent role in the control of circadian rhythm that displays anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-cancer, bone-protective, cardiovascular, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective and antipoxidant (free radical scavenging) properties. Melatonin functions as a glycolytic since it inhibits the Warburg effect. Melatonin may have advantages over the synthetic glycolytics since it is an endogenously synthesized molecule in every organism including in the human. Melatonin is also a mitophagy regulator. It seems to exert an essential effect on mitochondrial physiology and facilitates mitochondrial function. A central mechanism by which melatonin protects mitochondria is by restoring the MMP through blocking mPTP opening under stress and activating uncoupling proteins (UCPs) to marginally decrease MMP under normal conditions. Melatonin has also been proposed as an adjuvant in COVID-10 treatment, due to its anti-inflammatory properties and possible reduction of cytokine storm. Many biological effects of melatonin are transduced through melatonin receptors, including the MT1, MT2, and MT3 subtypes. Melatonin is a full agonist of melatonin receptor 1 (picomolar binding affinity) and melatonin receptor 2 (nanomolar binding affinity), both of which belong to the class of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). Melatonin receptors 1 and 2 are both Gi/o-coupled GPCRs, although melatonin receptor 1 is also Gq-coupled. Melatonin also acts as a high-capacity free radical scavenger within mitochondria which also promotes the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and catalase via signal transduction through melatonin receptors. Two main mechanisms have been put forward to explain the antioxidant and free radical properties of melatonin, by binding to the MT3 binding site and to the cytosolic enzyme quinone reductase 2 (QR2), and through the scavenging of free radicals, as this hormone has been suggested to be an electron donor. However, there are more than 15 proteins, including receptors (MT1, MT2, Mel1c, CAND2, ROR, VDR), enzymes (QR2, MMP-9, pepsin, PP2A, PR-10 proteins), pores (mtPTP), transporters (PEPT1/2, Glut1), and other proteins (HBS, CaM, tubulin, calreticuline), that have been suggested to interact with melatonin at sub-nanomolar to millimolar melatonin concentrations and could be responsible for some of its biological properties. - Melatonin is an endogeneous hormone that plays a prominent role in the control of circadian rhythm that displays anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-cancer, bone-protective, cardiovascular, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective and antipoxidant (free radical scavenging) properties. Melatonin functions as a glycolytic since it inhibits the Warburg effect. Melatonin may have advantages over the synthetic glycolytics since it is an endogenously synthesized molecule in every organism including in the human. Melatonin is also a mitophagy regulator. It seems to exert an essential effect on mitochondrial physiology and facilitates mitochondrial function. A central mechanism by which melatonin protects mitochondria is by restoring the MMP through blocking mPTP opening under stress and activating uncoupling proteins (UCPs) to marginally decrease MMP under normal conditions. Melatonin has also been proposed as an adjuvant in COVID-10 treatment, due to its anti-inflammatory properties and possible reduction of cytokine storm. Many biological effects of melatonin are transduced through melatonin receptors, including the MT1, MT2, and MT3 subtypes. Melatonin is a full agonist of melatonin receptor 1 (picomolar binding affinity) and melatonin receptor 2 (nanomolar binding affinity), both of which belong to the class of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). Melatonin receptors 1 and 2 are both Gi/o-coupled GPCRs, although melatonin receptor 1 is also Gq-coupled. Melatonin also acts as a high-capacity free radical scavenger within mitochondria which also promotes the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and catalase via signal transduction through melatonin receptors. Two main mechanisms have been put forward to explain the antioxidant and free radical properties of melatonin, by binding to the MT3 binding site and to the cytosolic enzyme quinone reductase 2 (QR2), and through the scavenging of free radicals, as this hormone has been suggested to be an electron donor. However, there are more than 15 proteins, including receptors (MT1, MT2, Mel1c, CAND2, ROR, VDR), enzymes (QR2, MMP-9, pepsin, PP2A, PR-10 proteins), pores (mtPTP), transporters (PEPT1/2, Glut1), and other proteins (HBS, CaM, tubulin, calreticuline), that have been suggested to interact with melatonin at sub-nanomolar to millimolar melatonin concentrations and could be responsible for some of its biological properties.
- SMILESCC(NCCC1=CNC2=CC=C(OC)C=C21)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Melatonin [73-31-4] [73-31-4]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/2F/CB/CgoaEWaDHeaEEgnuAAAAAAAnGtY678.png)