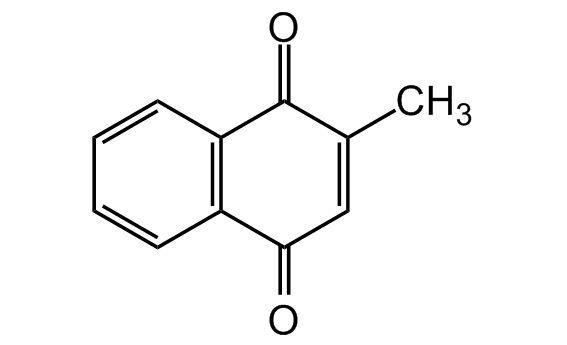
Chemical Structure
Menadione [58-27-5] [58-27-5]
AG-CR1-3631
CAS Number58-27-5
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight172.2
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameMenadione [58-27-5] [58-27-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number58-27-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC11H8O2
- Molecular Weight172.2
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 58-27-5. Formula: C11H8O2. MW: 172.2. Synthetic naphthoquinone without the isoprenoid side chain and biological activity, but can be converted to active vitamin K2 (menaquinone) after alkylation in vivo. The 1,4-naphthoquinone (NQ) moiety can form redox isomers by accepting one or two electrons respectively. The quinone redox cycling ability leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) as well as arylation reactions. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer in various cultured cells including leukemia through several modes of action. Free radical generator. Produces peroxide and superoxide radicals (ROS) leading to mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell cycle inhibitor. Glutathione (GSH) depletion results by direct arylation of cellular thiols. Once GSH is depleted, cellular macromolecules start to be alkylated, resulting in their inactivation. Protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Inhibitor of mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma. Inhibitor of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) with an IC50 of ~1microM. - Synthetic naphthoquinone without the isoprenoid side chain and biological activity, but can be converted to active vitamin K2 (menaquinone) after alkylation in vivo. The 1,4-naphthoquinone (NQ) moiety can form redox isomers by accepting one or two electrons respectively. The quinone redox cycling ability leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) as well as arylation reactions. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer in various cultured cells including leukemia through several modes of action. Free radical generator. Produces peroxide and superoxide radicals (ROS) leading to mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell cycle inhibitor. Glutathione (GSH) depletion results by direct arylation of cellular thiols. Once GSH is depleted, cellular macromolecules start to be alkylated, resulting in their inactivation. Protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Inhibitor of mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma. Inhibitor of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) with an IC50 of ~1microM.
- SMILESO=C1C(C)=CC(C2=C1C=CC=C2)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Menadione [58-27-5] [58-27-5]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/8C/CgoaEWY7MPaEfaghAAAAAGL-RRE336.png)