Chemical Structure
Muristerone A [38778-30-2]

AG-CN2-0070
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameMuristerone A [38778-30-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number38778-30-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
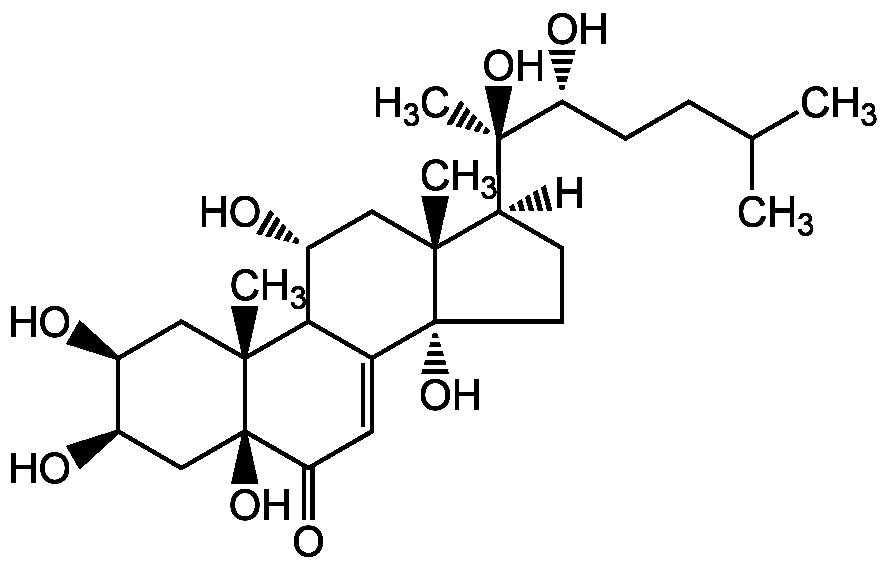
- Molecular FormulaC27H44O8
- Molecular Weight496.6
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 38778-30-2. Formula: C27H44O8. MW: 496.6. Isolated from Ipomoea hederacea seeds. Potent member of the ecdysteroid family. Ecdysone receptor (EcR) agonist. Analog of ecdysone with similar properties to ponasterone A (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0053 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cn2-0053/ponasterone-a.html ). Inducer of ecdysone-inducible gene expression systems in mammalian cells and transgenic animals. Induces apoptosis in cells transfected with wild-type Bax. Induces expression of beta-galactosidase. Stimulates Bcl-XL mRNA transcription and inhibits TRAIL- and hFasL-induced apoptosis in RKO cells. Insect steroid hormone involved in regulating metamorphosis, causing a response to G2 cell cycle arrest. Major molting hormone in some insects. Has protective effects in plants. - Potent member of the ecdysteroid family. Ecdysone receptor (EcR) agonist. Analog of ecdysone with similar properties to ponasterone A (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0053 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cn2-0053/ponasterone-a.html ). Inducer of ecdysone-inducible gene expression systems in mammalian cells and transgenic animals. Induces apoptosis in cells transfected with wild-type Bax. Induces expression of beta-galactosidase. Stimulates Bcl-XL mRNA transcription and inhibits TRAIL- and hFasL-induced apoptosis in RKO cells. Insect steroid hormone involved in regulating metamorphosis, causing a response to G2 cell cycle arrest. Major molting hormone in some insects. Has protective effects in plants.
- SMILES[H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2(O)C3=CC(=O)[C@]4(O)C[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)C[C@]4(C)C3[C@H](O)C[C@]12C)[C@@](C)(O)[C@H](O)CCC(C)C
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Structure of muristerone A, a new phytoecdysone: L. Canonica, et al.; J. C. S. Chem. Commun. 1060 (1972)
- New phytoecdysones from kaladana. I. Structure of muristerone A and kaladasterone: L. Canonica, et al.; Gazz. Chim. Ital. 107, 123 (1977)
- Characterization and partial purification of the Drosophila Kc cell ecdysteroid receptor: T.M. Landon, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 263, 4693 (1988)
- Ecdysteroid-Dependent Regulation of Genes in Mammalian Cells by a Drosophila Ecdysone Receptor and Chimeric Transactivators: K. Christopherson, et al.; PNAS 89, 6314 (1992)
- Ecdysone-inducible gene expression in mammalian cells and transgenic mice: D. No, et al.; PNAS 93, 3346 (1996)
- The overexpression of Bax produces cell death upon induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition: J.G. Pastorino, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 273, 7770 (1998)
- Impairment of the proapoptotic activity of Bax by missense mutations found in gastrointestinal cancers: J. Gil, et al.; Cancer Res. 59, 2034 (1999)
- Identification of ligands and coligands for the ecdysone-regulated gene switch: E. Saez, et al.; PNAS 97, 14512 (2000)
- Ectopic expression of cyclin D1 impairs the proliferation and enhances the apoptosis of a murine lymphoid cell line: F. Duquesne, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 8, 51 (2001)
- The ecdysone inducible gene expression system: unexpected effects of muristerone A and ponasterone A on cytokine signaling in mammalian cells: S. Constantino, et al.; Eur. Cytokine Netw. 12, 365 (2001)
