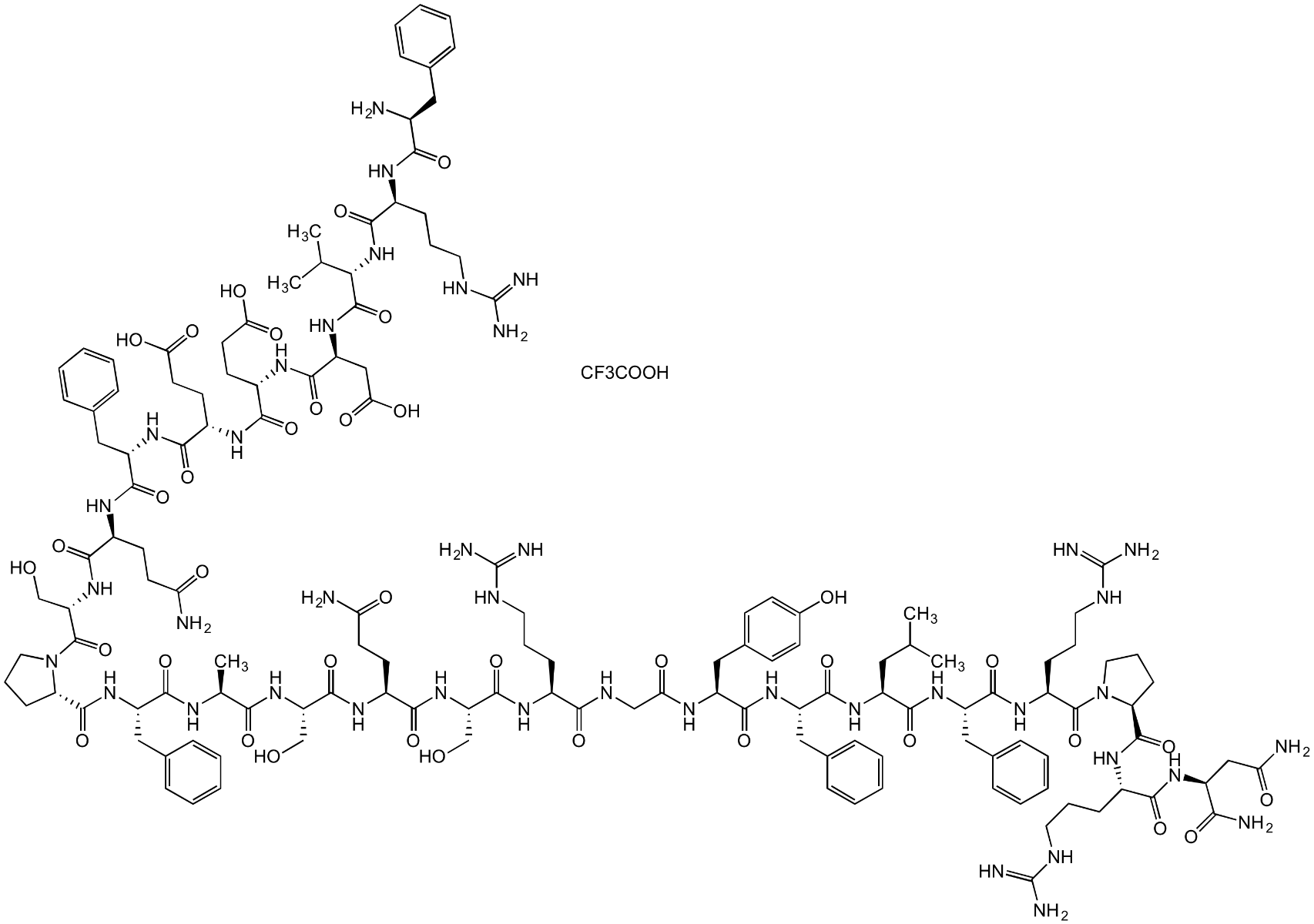
Chemical Structure
Neuromedin U-25 (human) [312306-89-1] [312306-89-1]
AG-CP3-0031
CAS Number312306-89-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight3080.4 . 114.0
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameNeuromedin U-25 (human) [312306-89-1] [312306-89-1]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number312306-89-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC141H203N41O38 . C2HF3O2
- Molecular Weight3080.4 . 114.0
- Scientific DescriptionActive human form of NMU. Binds to two high affinity G-protein coupled receptors, NMUR1 and NMUR2, with NMUR1 predominantly expressed in the peripheral tissues and NMUR2 mainly expressed in the CNS. The activation of NMURs leads to intracellular signal transduction via calcium mobilization, phosphoinositide (or PI) signaling and the inhibition of cAMP production and therefore has diverse functions including contraction of smooth muscle, vasoconstriction, nociception, appetite and bone remodeling. Implicated in a number of physiological processes including the regulation of feeding, energy homeostasis and glycemic control and therefore used to target obesity and diabetes. Activator of innate lymphoid cells 2 (ILC2) during inflammation, as shown in studies in mice [6-8]. - Chemical. CAS: 312306-89-1. Formula: C141H203N41O38 . C2HF3O2. MW: 3080.4 . 114.0. Synthetic. Active human form of NMU. Binds to two high affinity G-protein coupled receptors, NMUR1 and NMUR2, with NMUR1 predominantly expressed in the peripheral tissues and NMUR2 mainly expressed in the CNS. The activation of NMURs leads to intracellular signal transduction via calcium mobilization, phosphoinositide (or PI) signaling and the inhibition of cAMP production and therefore has diverse functions including contraction of smooth muscle, vasoconstriction, nociception, appetite and bone remodeling. Implicated in a number of physiological processes including the regulation of feeding, energy homeostasis and glycemic control and therefore used to target obesity and diabetes. Activator of innate lymphoid cells 2 (ILC2) during inflammation, as shown in studies in mice.
- SMILESC[C@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H]1CCCN1C([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](N)CC2=CC=CC=C2)=O)CCCNC(N)=N)=O)C(C)C)=O)CC(O)=O)=O)CCC(O)=O)=O)CCC(O)=O)=O)CC3=CC=CC=C3)=O)CCC(N)=O)=O)CO)=O)=O)CC4=CC=CC=C4)=O)C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(NCC(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N5CCC[C@H]5C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N)=O)CC(N)=O)=O)CCCNC(N)=N)=O)=O)CCCNC(N)=N)=O)CC6=CC=CC=C6)=O)CC(C)C)=O)CC7=CC=CC=C7)=O)CC8=CC=C(O)C=C8)=O)=O)CCCNC(N)=N)=O)CO)=O)CCC(N)=O)=O)CO)=O.FC(F)(C(O)=O)F
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Neuromedin U-25 (human) [312306-89-1] [312306-89-1]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/38/30/CgoaEGa8jzCEUzVjAAAAAEbykTg916.png)