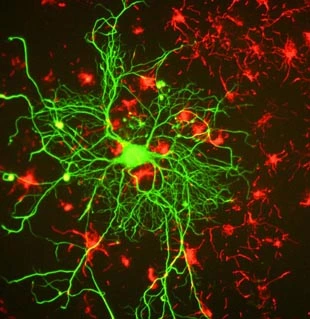
Cells grown from adult rat brain. Large cell in middle is stained with mouse monoclonal to NF-L clone DA2 (green). Another type of neuronal lineage cell was stained with rabbit polyclonal to alpha-internexin?RPCa-a-Int?(red). These cells were mitotic but had several characteristics of neurons.
NF-L antibody [DA2]
GTX24572
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Rat
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameNF-L antibody [DA2]
- Delivery Days Customer7
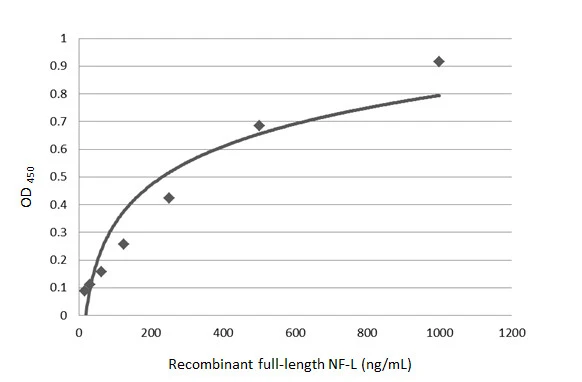
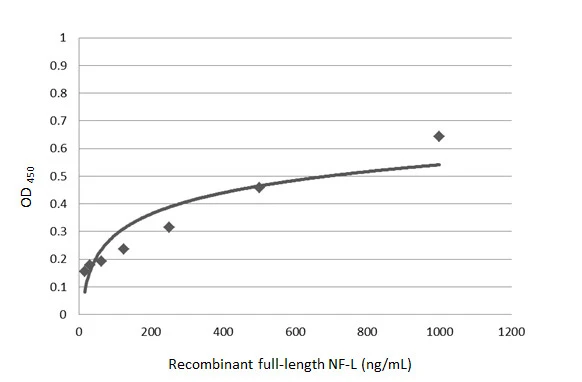
- Antibody SpecificityScreening was performed by ELISA using the immunogen, followed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Clones which revealed strong staining were further characterized biochemically.
- Application Supplier NoteIF: Use at a dilution of 1/100 - 1/500. IHC-Fr: Use at an assay dependant dilution. WB: Use at a dilution of 1/5000 - 1/10000. Predicted molecular weight: 68 kDa. Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDDA2
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
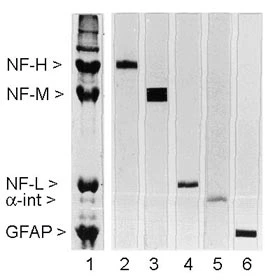
- Scientific DescriptionNeurofilaments are the 10nm or intermediate filament proteins found specifically in neurons, and are composed predominantly of three major proteins called NF-L, NF-M and NF-H. NF-L is the neurofilament light or low molecular weight polypeptide and runs on SDS-PAGE gels at about 68kDa. Antibodies to NF-L are useful for identifying neuronal cells and their processes in tissue sections and in tissue culture. NF-L antibody can also be useful in the diagnostics of neurofilament accumulations seen in many neurological diseases, such as Lou Gehrigs disease or Alzheimers disease. Mutations in the protein coding region of the human NF-L gene appear to cause some forms of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
- ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203