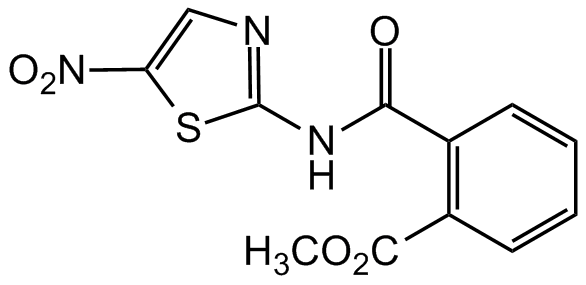
Chemical Structure
Nitazoxanide
AG-CR1-3723
CAS Number55981-09-4
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight307.3
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameNitazoxanide
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number55981-09-4
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC12H9N3O5S
- Molecular Weight307.3
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 55981-09-4. Formula: C12H9N3O5S. MW: 307.3. Nitazoxanide is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic, antimicrobial and antiviral drug that is used in medicine for the treatment of various helminthic, protozoal, bacterial and viral infections. Nitazoxanide is rapidly metabolized to tizaxonide, an antiparasitic drug of the thiazolide class. The anti-protozoal activity and activity against anaerobic bacteria is believed to be due to interference with the pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR) enzyme-dependent electron transfer reaction which is essential to anaerobic energy metabolism. Nitazoxanide also showed a variety of other antibacterial mechanisms, inhibiting pyruvate dehydrogenase in E. coli, disrupting the membrane potential and pH homeostasis in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis and suppressing the chaperone/usher (CU) pathway of the Gram-negative bacteria. It is being studied for potential treatment for chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C, rotavirus, norovirus gastroenteritis and the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). The mechanism is suppressing the viral replication by inhibiting maturation of the viral hemagglutinin and the viral transcription factor immediate early 2 (IE2) as well as by activating the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha (an antiviral intracellular protein). Nitazoxanide modulates a variety of other pathways in vitro, including glutathione-S-transferase and glutamate-gated chloride ion channels in nematodes, respiration and other pathways in bacteria and cancer cells and viral and host transcriptional factors. Nitazoxanide has also been shown to be a potent antagonist of the Ca2+-activated Cl- channel TMEM16A, which offers a new mechanism to bronchodilate airways and block the multiple contractiles operating in severe diseases. - Nitazoxanide is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic, antimicrobial and antiviral drug that is used in medicine for the treatment of various helminthic, protozoal, bacterial and viral infections. Nitazoxanide is rapidly metabolized to tizaxonide, an antiparasitic drug of the thiazolide class. The anti-protozoal activity and activity against anaerobic bacteria is believed to be due to interference with the pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR) enzyme-dependent electron transfer reaction which is essential to anaerobic energy metabolism. Nitazoxanide also showed a variety of other antibacterial mechanisms, inhibiting pyruvate dehydrogenase in E. coli, disrupting the membrane potential and pH homeostasis in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis and suppressing the chaperone/usher (CU) pathway of the Gram-negative bacteria. It is being studied for potential treatment for chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C, rotavirus, norovirus gastroenteritis and the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). The mechanism is suppressing the viral replication by inhibiting maturation of the viral hemagglutinin and the viral transcription factor immediate early 2 (IE2) as well as by activating the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha (an antiviral intracellular protein). Nitazoxanide modulates a variety of other pathways in vitro, including glutathione-S-transferase and glutamate-gated chloride ion channels in nematodes, respiration and other pathways in bacteria and cancer cells and viral and host transcriptional factors. Nitazoxanide has also been shown to be a potent antagonist of the Ca2+-activated Cl- channel TMEM16A, which offers a new mechanism to bronchodilate airways and block the multiple contractiles operating in severe diseases.
- SMILESO=C(NC1=NC=C([N+]([O-])=O)S1)C2=C(C(OC)=O)C=CC=C2
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Nitazoxanide [55981-09-4]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/03/43/CgoaEWY7RkuEArNlAAAAAFEcgfE984.png)