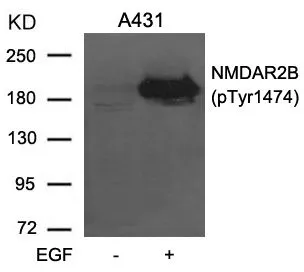
WB analysis of extracts from A431 cells untreated or treated with EGF using GTX50221 NMDAR2B (phospho Tyr1472) antibody.
NMDAR2B (phospho Tyr1472) antibody
GTX50221
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetGRIN2B
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameNMDAR2B (phospho Tyr1472) antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:1000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2904
- Target nameGRIN2B
- Target descriptionglutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 2B
- Target synonymsDEE27, EIEE27, GluN2B, MRD6, NMDAR2B, NR2B, NR3, hNR3, glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2B, GluN2B(alt_5'UTR), N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 3, glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-2, glutamate receptor subunit epsilon-2, glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2B
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ13224
- Protein NameGlutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2B
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor family within the ionotropic glutamate receptor superfamily. The encoded protein is a subunit of the NMDA receptor ion channel which acts as an agonist binding site for glutamate. The NMDA receptors mediate a slow calcium-permeable component of excitatory synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. The NMDA receptors are heterotetramers of seven genetically encoded, differentially expressed subunits including NR1 (GRIN1), NR2 (GRIN2A, GRIN2B, GRIN2C, or GRIN2D) and NR3 (GRIN3A or GRIN3B). The early expression of this gene in development suggests a role in brain development, circuit formation, synaptic plasticity, and cellular migration and differentiation. Naturally occurring mutations within this gene are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders including autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, epilepsy, and schizophrenia. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203



![NMDAR2B antibody [HL3166] detects NMDAR2B protein by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV11 rat E18 primary hippocampal neuron cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: NMDAR2B stained by NMDAR2B antibody [HL3166] (GTX640676) diluted at 1:250. Red: Tau, an axon marker, stained by Tau antibody [GT287] (GTX634809) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX640676/GTX640676_T-45481_20241122_ICC_IF_R_24120522_468.webp)
