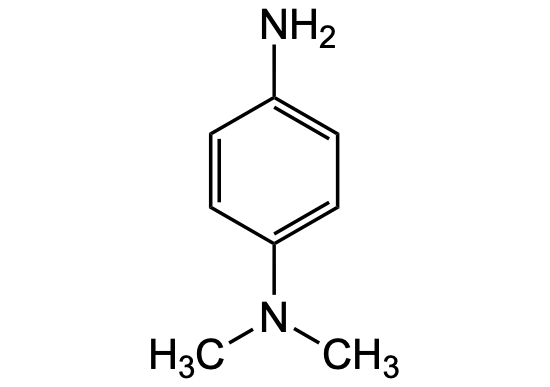
Chemical Structure
N,N-Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine [99-98-9] [99-98-9]
CDX-D0898
CAS Number99-98-9
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97%
Molecular Weight136.19
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameN,N-Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine [99-98-9] [99-98-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number99-98-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC8H12N2
- Molecular Weight136.19
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 99-98-9. Formula: C8H12N2. MW: 136.19. N,N-Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine (DMPD) is a redox/oxidative stress indicator. It readily forms stable radical cations, involved in a variety of redox reactions. Has also been used to quantify labile sulfide in proteins, to detect sterolhydroperoxides, and for the measure of the antioxidant activity and used as an intermediate to produce dyes. DMPD is being explored for colorimetric detection of various analytes, especially in antioxidant assays. The principle of the assay is that at an acidic pH and in the presence of a suitable oxidant solution DMPD can form a stable and colored radical cation (DMPD+). Antioxidant compounds which are able to transfer a hydrogen atom to DMPD+ quench the color and produce a decoloration of the solution which is proportional to their amount. This reaction is rapid (less than 10 min) and the end point, which is stable, is taken as a measure of the antioxidative efficiency. Used to determine the oxidative status of plasma or serum samples. Also one of the most successful and frequently used method for sulfide determination as a consequence of its inherent specificity relies upon the oxidative coupling of sulfide ions with DMPD in the presence of Fe(III)-Fischers reaction to form the methylene blue (MB) dye. - N,N-Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine (DMPD) is a redox/oxidative stress indicator. It readily forms stable radical cations, involved in a variety of redox reactions. Has also been used to quantify labile sulfide in proteins, to detect sterolhydroperoxides, and for the measure of the antioxidant activity and used as an intermediate to produce dyes. DMPD is being explored for colorimetric detection of various analytes, especially in antioxidant assays. The principle of the assay is that at an acidic pH and in the presence of a suitable oxidant solution DMPD can form a stable and colored radical cation (DMPD+). Antioxidant compounds which are able to transfer a hydrogen atom to DMPD+ quench the color and produce a decoloration of the solution which is proportional to their amount. This reaction is rapid (less than 10 min) and the end point, which is stable, is taken as a measure of the antioxidative efficiency. Used to determine the oxidative status of plasma or serum samples. Also one of the most successful and frequently used method for sulfide determination as a consequence of its inherent specificity relies upon the oxidative coupling of sulfide ions with DMPD in the presence of Fe(III)-Fischers reaction to form the methylene blue (MB) dye.
- SMILESCN(C)c1ccc(N)cc1
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UN NumberUN2811
- UNSPSC12162000
