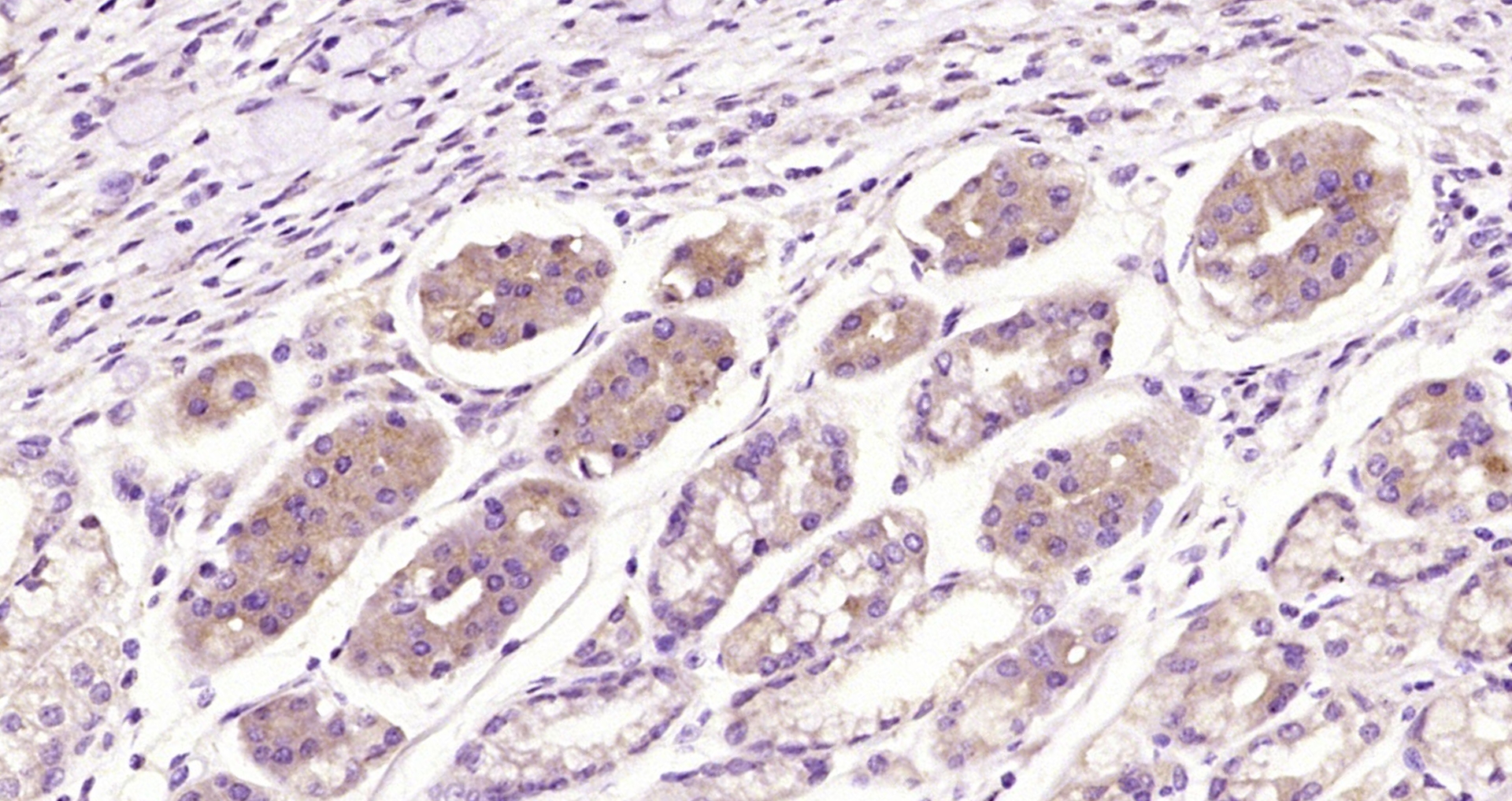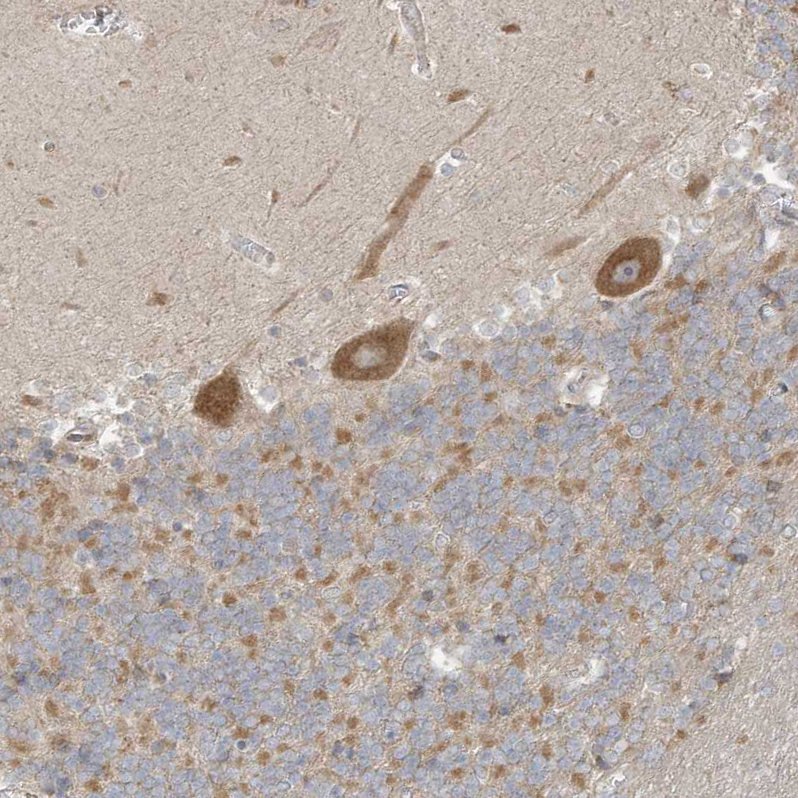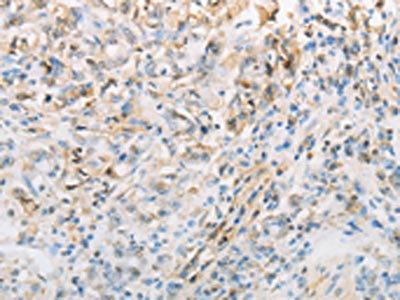
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human gastic cancer tissue using CSB-PA136609(NPPC Antibody) at dilution 1/70, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200)
NPPC Antibody
CSB-PA136609
ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetNPPC
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NameNPPC Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID4880
- Target nameNPPC
- Target descriptionnatriuretic peptide C
- Target synonymsCNP, CNP2, C-type natriuretic peptide, natriuretic peptide precursor type C
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP23582
- Protein NameC-type natriuretic peptide
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the Notch family. Members of this Type 1 transmembrane protein family share structural characteristics including an extracellular domain consisting of multiple epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) repeats, and an intracellular domain consisting of multiple, different domain types. Notch family members play a role in a variety of developmental processes by controlling cell fate decisions. The Notch signaling network is an evolutionarily conserved intercellular signaling pathway which regulates interactions between physically adjacent cells. In Drosophilia, notch interaction with its cell-bound ligands (delta, serrate) establishes an intercellular signaling pathway that plays a key role in development. Homologues of the notch-ligands have also been identified in human, but precise interactions between these ligands and the human notch homologues remain to be determined. This protein is cleaved in the trans-Golgi network, and presented on the cell surface as a heterodimer. This protein functions as a receptor for membrane bound ligands, and may play a role in vascular, renal and hepatic development. This gene may be associated with susceptibility to schizophrenia in a small portion of cases. An alternative splice variant has been described but its biological nature has not been determined.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC41116161