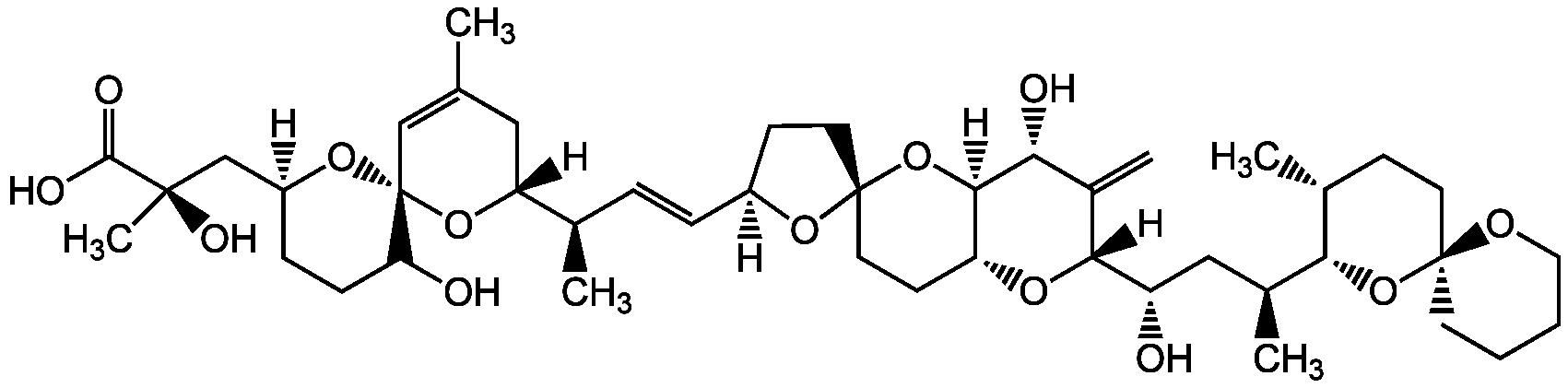
Chemical Structure
Okadaic acid (high purity) [78111-17-8]

AG-CN2-0056
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameOkadaic acid (high purity) [78111-17-8]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ADR Class6.1
- CAS Number78111-17-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC44H68O13
- Molecular Weight805
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 78111-17-8. Formula: C44H68O13. MW: 805. Isolated from Prorocentrum concavum. Non-phorbol type tumor promoter. Reversible, potent and selective serine threonine protein phosphatase inhibitor. PP2A (IC50=0.2-1nM), PP1 (IC50=3-15nM), PP2B (IC50=>1microM). Does not inhibit PP2C. Stimulates intracellular protein phosphorylation. Useful tool for studying cellular processes that are regulated by phosphorylation. Does not affect activity of acid phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase and tyrosine phosphatase. Mimics the effects of insulin. Activates atypical protein kinase C (zeta/lambda) in 3T3/L1 adipocytes. Enhances transmitter release at neuromuscular junctions. Apoptosis inhibitor. Induces apoptosis in human breast carcinoma cells (MB-231 and MCF-7) and in myeloid cells. Neurotoxic. Used to study various cellular processes including cell cycle, apoptosis, nitric oxide metabolism and calcium signaling. Stimulates cell motility, loss of stabilization of focal adhesions and a consequent loss of cytoskeletal organization. - Non-phorbol type tumor promoter [1]. Reversible, potent and selective serine threonine protein phosphatase inhibitor. PP2A (IC50=0.2-1nM), PP1 (IC50=3-15nM), PP2B (IC50=>1microM). Does not inhibit PP2C [2, 6, 7, 18]. Stimulates intracellular protein phosphorylation [3]. Useful tool for studying cellular processes that are regulated by phosphorylation. Does not affect activity of acid phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase and tyrosine phosphatase [4, 5]. Mimics the effects of insulin [7]. Activates atypical protein kinase C (zeta/lambda) in 3T3/L1 adipocytes [14, 19]. Enhances transmitter release at neuromuscular junctions [8]. Apoptosis inhibitor [9, 11, 12]. Induces apoptosis in human breast carcinoma cells (MB-231 and MCF-7) and in myeloid cells [10]. Neurotoxic [12, 16]. Used to study various cellular processes including cell cycle, apoptosis, nitric oxide metabolism and calcium signaling [13, 15, 17, 18]. Stimulates cell motility, loss of stabilization of focal adhesions and a consequent loss of cytoskeletal organization [20].
- SMILES[H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2(CC[C@H]3O[C@@]([H])([C@@H](O)C[C@H](C)[C@H]4O[C@@]5(CCCCO5)CC[C@H]4C)C(=C)[C@@H](O)[C@]3([H])O2)O1)\C=C\[C@@H](C)[C@@]1([H])CC(C)=C[C@@]2(O[C@]([H])(C[C@@](C)(O)C(O)=O)CCC2O)O1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UN NumberUN 3462
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Okadaic acid: an additional non-phorbol-12-tetradecanoate-13-acetate- type tumor promoter: M. Suganuma, et al.; PNAS 85, 1768 (1988)
- Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics: C. Bialojan & A. Takai; Biochem. J. 256, 283 (1988)
- Effects of the tumour promoter okadaic acid on intracellular protein phosphorylation and metabolism: T.A. Haystead, et al.; Nature 337, 78 (1989)
- An improved procedure for identifying and quantitating protein phosphatases in mammalian tissues: P. Cohen, et al.; FEBS Lett. 250, 596 (1989)
- Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation: P. Cohen, et al.; TIPS 15, 98 (1990) (Review)
- Use of okadaic acid to inhibit protein phosphatases in intact cells: D.G. Hardie, et al.; Methods Enzymol. 201, 469 (1991)
- Effects of okadaic acid, an inhibitor of protein phosphatases-1 and -2A, on glucose transport and metabolism in skeletal muscle: J.F. Tanti, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 266, 2099 (1991)
- Protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid enhances transmitter release at neuromuscular junctions: M. Abdul-Ghani, et al.; PNAS 88, 1803 (1991)
- Inhibition of apoptosis in human tumour cells by okadaic acid: Q. Song, et al.; J. Cell Physiol. 153, 550 (1992)
- Differential induction of apoptosis in human breast tumor cells by okadaic acid and related inhibitors of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A: K. Kiguchi, et al.; Cell Growth Differentiation 5, 995 (1994)
