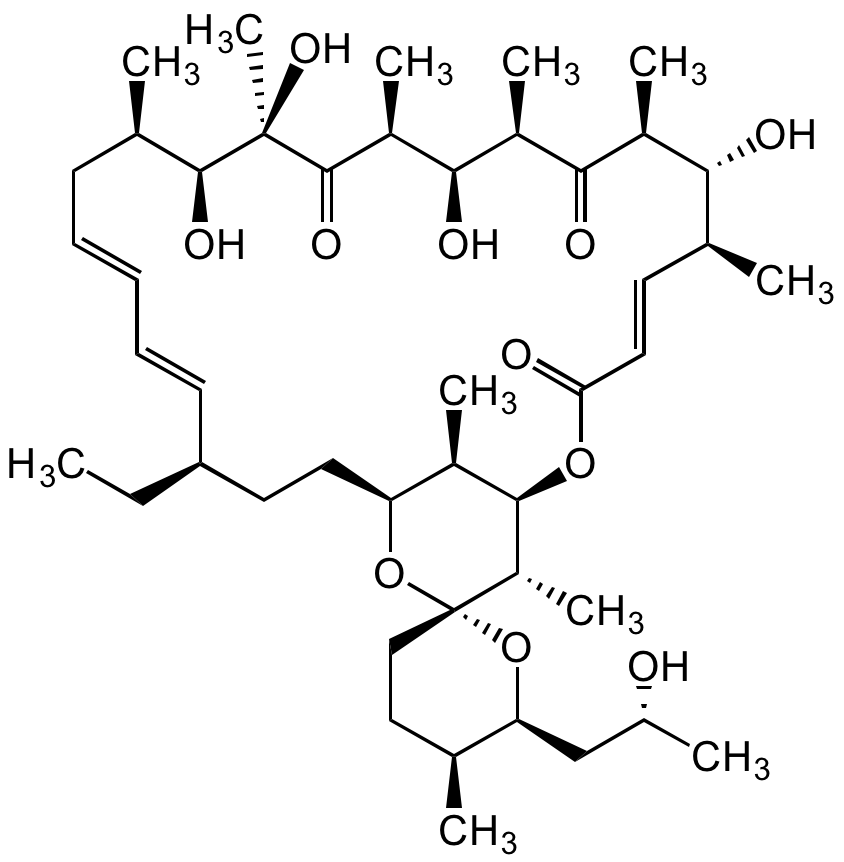
Chemical Structure
Oligomycin A [579-13-5]

AG-CN2-0517
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameOligomycin A [579-13-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number579-13-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC45H74O11
- Molecular Weight791.1
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 579-13-5. Formula: C45H74O11. MW: 791.1. Synthetic. Originally isolated from Streptomyces diastatochromogenes. Potent mitochondrial ATP synthase (ATPases (F1F0)) inhibitor, consequently leading to inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Inhibits ATP synthase by blocking its proton channel (F0 subunit), which is necessary for oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP (energy production), significantly reducing electron flow through the electron transport chain. Anticancer agent. Shown to induce apoptosis/necroptosis in a variety of cell types, as well as autophagy. Shown to activate AMPK. Broad antifungal, antibiotic and nematocidal agent. - Potent mitochondrial ATP synthase (ATPases (F0F1)) inhibitor, consequently leading to inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Inhibits ATP synthase by blocking its proton channel (F0 subunit), which is necessary for oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP (energy production), significantly reducing electron flow through the electron transport chain. Anticancer agent. Shown to induce apoptosis/necroptosis in a variety of cell types, as well as autophagy. Shown to activate AMPK. Broad antifungal, antibiotic and nematocidal agent.
- SMILESC[C@H]1CC[C@@]2([C@@H](C)[C@H](OC(/C=C/[C@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)C([C@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]3C)=O)=O)[C@H](C)[C@H](CC[C@@H](CC)/C=C/C=C/C[C@@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@@](C)(O)C3=O)O2)O[C@H]1C[C@H](O)C
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Oligomycin, a new antifungal antibiotic: R.M. Smith, et al.; Antibiot. Chemother. 4, 962 (1954)
- The use of oligomycin as an inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation: F. Huijing & E.C. Slater; J. Biochem. 49, 493 (1961)
- Inhibitors of the ATP synthethase system: P.E. Linnett & R.B. Beechey; Methods Enzymol. 55, 472 (1979)
- Apoptolidin, a selective cytotoxic agent, is an inhibitor of F0F1-ATPase: A.R. Salomon, et al.; Chem. Biol. 8, 71 (2001)
- Oligomycin, inhibitor of the F0 part of H+-ATP-synthase, suppresses the TNF-induced apoptosis: L.A. Shchepina, et al.; Oncogene 21, 8149 (2002)
- Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Leads to the Phosphorylation of Elongation Factor 2 and an Inhibition of Protein Synthesis: S. Horman, et al.; Curr. Biol. 12, 1419 (2002)
- Down-regulation of mitochondrial F1F0-ATP synthase in human colon cancer cells with induced 5-fluorouracil resistance: Y.K. Shin, et al.; Cancer Res. 65, 3162 (2005)
- Oligomycin A induces autophagy in the IPLB-LdFB insect cell line: G. Tettamanti, et al.; Cell Tissue Res. 326, 179 (2006)
- Age-dependent cell death and the role of ATP in hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis and necrosis: N. Miyoshi, et al.; PNAS 103, 1727 (2006)
- A new strain of Streptomyces avermitilis produces high yield of oligomycin A with potent anti-tumor activity on human cancer cell lines in vitro: X. Lin, et al.; Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 81, 839 (2009)
