![p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein(TP53/3156R), CF594 conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8] p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein(TP53/3156R), CF594 conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]](https://biotium.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/view_image-884.jpeg)
p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein(TP53/3156R), CF594 conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]
BNC943156
ReactivityCanine, Hamster, Human, Monkey, Mouse, Rat
Product group Antibodies
TargetTP53
Overview
- SupplierBiotium
- Product Namep53 Tumor Suppressor Protein(TP53/3156R), CF594 conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- CAS Number26628-22-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDTP53/3156R
- Concentration0.1 mg/ml
- ConjugateOther Conjugate
- Gene ID7157
- Target nameTP53
- Target descriptiontumor protein p53
- Target synonymsBCC7, BMFS5, LFS1, P53, TRP53, cellular tumor antigen p53, antigen NY-CO-13, mutant tumor protein 53, phosphoprotein p53, transformation-related protein 53, tumor protein 53, tumor supressor p53
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP04637
- Protein NameCellular tumor antigen p53
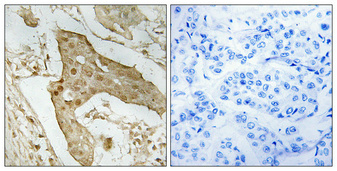
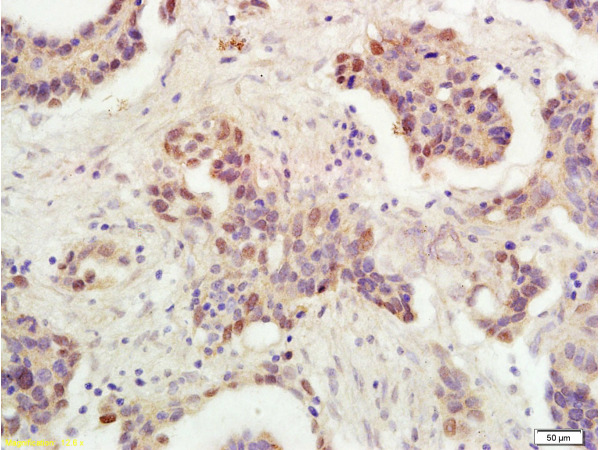
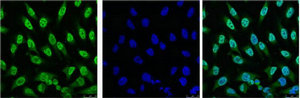
- Scientific DescriptionThe specificity of this monoclonal antibody to its intended target was validated by HuProt™ Array, containing more than 19, 000, full-length human proteins. TP53/3156R binds to the C-terminus (aa370-378) of both wild type and mutated p53. When microinjected into nuclei, TP53/3156R blocked re-entry into the S-phase of the cell cycle. Mutation and/or allelic loss of p53 is one of the causes of a variety of mesenchymal and epithelial tumors. If it occurs in the germ line, such tumors run in families. p53 Binds to a DNA consensus sequence, the p53 response element, and it regulates normal cell growth cycle events by activating transcription of genes, involved either in progression through the cycle, or causing arrest in G1 when the genome is damaged. In most transformed and tumor cells the concentration of p53 is increased 51000 fold over the minute concentrations (1000 molecules cell) in normal cells, principally due to the increased half-life (4 h) compared to that of the wild-type (20 min). p53 Localizes in the nucleus, but is detectable at the plasma membrane during mitosis and when certain mutations modulate cytoplasmic/nuclear distribution. p53 Is the most commonly mutated gene in spontaneously occurring human cancers. Mutations arise with an average frequency of 70% but incidence varies from zero in carcinoid lung tumors to 97% in primary melanomas. High concentrations of p53 protein are transiently expressed in human epidermis and superficial dermal fibroblasts following mild ultraviolet irradiation. Primary antibodies are available purified, or with a selection of fluorescent CF® Dyes and other labels. CF® Dyes offer exceptional brightness and photostability. Note: Conjugates of blue fluorescent dyes like CF®405S and CF®405M are not recommended for detecting low abundance targets, because blue dyes have lower fluorescence and can give higher non-specific background than other dye colors.
- SourceAnimal
- ReactivityCanine, Hamster, Human, Monkey, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC41116161