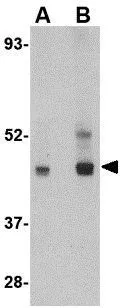
PAFAH1B1 Antibody, HRP conjugated
CSB-PA017383LB01HU
ApplicationsELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetPAFAH1B1
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NamePAFAH1B1 Antibody, HRP conjugated
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateHRP
- Gene ID5048
- Target namePAFAH1B1
- Target descriptionplatelet activating factor acetylhydrolase 1b regulatory subunit 1
- Target synonymsLIS1, LIS2, MDCR, MDS, NudF, PAFAH, platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit beta, lissencephaly 1 protein, platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase 1b, regulatory subunit 1 (45kDa)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP43034
- Protein NamePlatelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit beta
- Scientific DescriptionRequired for proper activation of Rho GTPases and actin polymerization at the leading edge of locomoting cerebellar neurons and postmigratory hippocampal neurons in response to calcium influx triggered via NMDA receptors. Non-catalytic subunit of an acetylhydrolase complex which inactivates platelet-activating factor (PAF) by removing the acetyl group at the SN-2 position (By similarity). Positively regulates the activity of the minus-end directed microtubule motor protein dynein. May enhance dynein-mediated microtubule sliding by targeting dynein to the microtubule plus end. Required for several dynein- and microtubule-dependent processes such as the maintenance of Golgi integrity, the peripheral transport of microtubule fragments and the coupling of the nucleus and centrosome. Required during brain development for the proliferation of neuronal precursors and the migration of newly formed neurons from the ventricular/subventricular zone toward the cortical plate. Neuronal migration involves a process called nucleokinesis, whereby migrating cells extend an anterior process into which the nucleus subsequently translocates. During nucleokinesis dynein at the nuclear surface may translocate the nucleus towards the centrosome by exerting force on centrosomal microtubules. May also play a role in other forms of cell locomotion including the migration of fibroblasts during wound healing.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC41116161