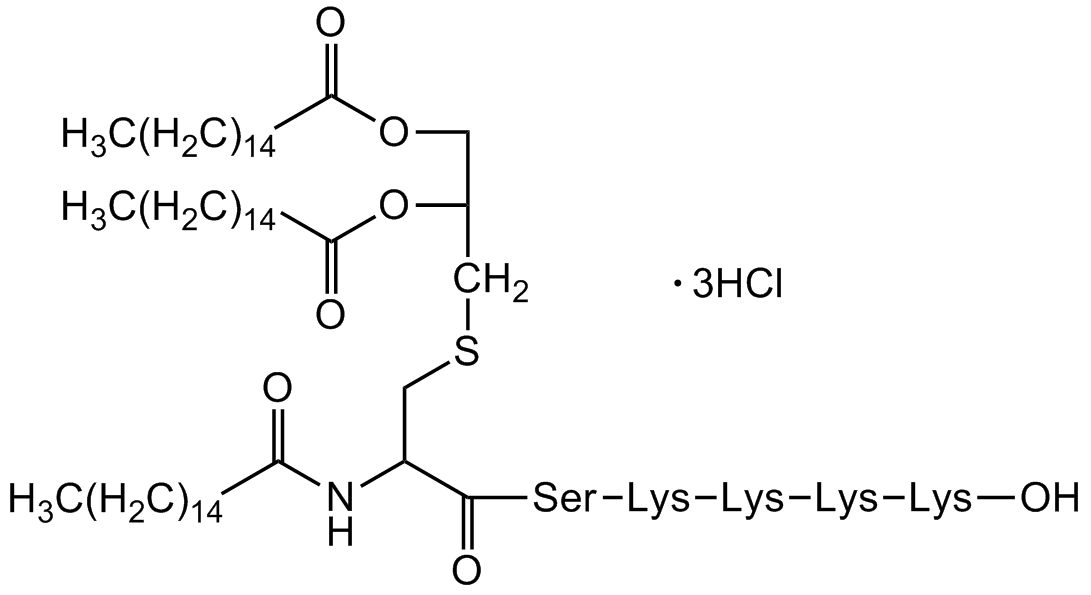
Chemical Structure
Pam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4 . trihydrochloride [112208-00-1]

AG-CP3-0003
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NamePam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4 . 3HCl [112208-04-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number112208-00-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC81H156N10O13S . 3HCl
- Molecular Weight1510.3 . 109.4
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 112208-04-5. Formula: C81H156N10O13S . 3HCl. MW: 1510.3 . 109.4. Synthetic. Selective agonist of TLR1/TLR2 complex. Cell permeable, water soluble synthetic cationic lipohexapeptide analog of the immunologically active N-terminal portion of bacterial lipoprotein that potently activates monocytes and macrophages. Potent and effective immune adjuvant. Exerts strong local response, enhances IgG2a and IgG1 titers and upregulates proinflammatory and Th1 cytokine genes. Potent activator of the proinflammatory transcription factor NF-kappaB. - Selective agonist of TLR1/TLR2 complex. Cell permeable, water soluble synthetic cationic lipohexapeptide analog of the immunologically active N-terminal portion of bacterial lipoprotein that potently activates monocytes and macrophages. Potent and effective immune adjuvant. Exerts strong local response, enhances IgG2a and IgG1 titers and upregulates proinflammatory and Th1 cytokine genes. Potent activator of the proinflammatory transcription factor NF-kappaB.
- SMILESCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)NC(CSCC(COC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)C(=O)[C@H](CCCCN)NN[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(O)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Lipopeptide derivatives of bacterial lipoprotein constitute potent immune adjuvants combined with or covalently coupled to antigen or hapten: A. Reitermann, et al.; Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 370, 343 (1989)
- Induction of tumor cytotoxicity in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages by two synthetic lipopeptide analogues: P. Hoffmann, et al.; Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 370, 575 (1989)
- Activation of superoxide formation and lysozyme release in human neutrophils by the synthetic lipopeptide Pam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4. Involvement of guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins and synergism with chemotactic peptides: R. Seifert, et al.; Biochem. J. 267, 795 (1990)
- Synthesis of novel immunologically active tripalmitoyl-S-glycerylcysteinyl lipopeptides as useful intermediates for immunogen preparations: J. Metzger, et al.; Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 37, 46 (1991)
- The influence of various adjuvants on antibody synthesis following immunization with an hapten: J. Kellner, et al.; Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 373, 51 (1992)
- Lipopeptides are effective stimulators of tyrosine phosphorylation in human myeloid cells: S. Offermanns, et al.; Biochem. J. 282, 551 (1992)
- Comparison of adjuvant formulations for cytotoxic T cell induction using synthetic peptides: C.E. Hioe, et al.; Vaccine 14, 412 (1996)
- Cell Activation and Apoptosis by Bacterial Lipoproteins Through Toll-like Receptor-2: A.O. Aliprantis, et al.; Science 285, 736 (1999)
- Adjuvant effects of various lipopeptides and interferon-gamma on the humoral immune response of chickens: M.H. Erhard, et al.; Poult. Sci. 79, 1264 (2000)
- Immunostimulation by the synthetic lipopeptide P3CSK4: TLR4-independent activation of the ERK1/2 signal transduction pathway in macrophages: M.R. Muller, et al.; Immunology 103, 49 (2001)
