Chemical Structure
Pepstatin A [26305-03-3]

AG-CP3-7001
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NamePepstatin A [26305-03-3]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number26305-03-3
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC34H63N5O9
- Molecular Weight685.9
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 26305-03-3. Formula: C34H63N5O9. MW: 685.9. Synthetic. Tight-binding, reversible, highly selective inhibitor of acid proteases (aspartyl peptidases), like pepsin, gastricsin, cathepsin E and D, renin, chymosin, bacterial aspartic proteinases and HIV proteases. Does not inhibit thiol proteases, neutral proteases or serine proteases. Widely used as a research tool in studies of protease mechanisms and biological functions. Solubilized gamma-secretase and retroviral protease inhibitor. Shows antibacterial, antifungal and antiparasitic activity. Suppresses p53-dependent apoptosis in lymphoid cells as well as TNFalpha-induced apoptosis in U937 cells. Inhibits degradation of autophagic cargo inside autophagolysosomes. - Tight-binding, reversible, highly selective inhibitor of acid proteases (aspartyl peptidases), like pepsin, gastricsin, cathepsin E and D, renin, chymosin, bacterial aspartic proteinases and HIV proteases. Does not inhibit thiol proteases, neutral proteases or serine proteases. Widely used as a research tool in studies of protease mechanisms and biological functions. Solubilized gamma-secretase and retroviral protease inhibitor. Shows antibacterial, antifungal and antiparasitic activity. Suppresses p53-dependent apoptosis in lymphoid cells as well as TNFalpha-induced apoptosis in U937 cells. Inhibits degradation of autophagic cargo inside autophagolysosomes.
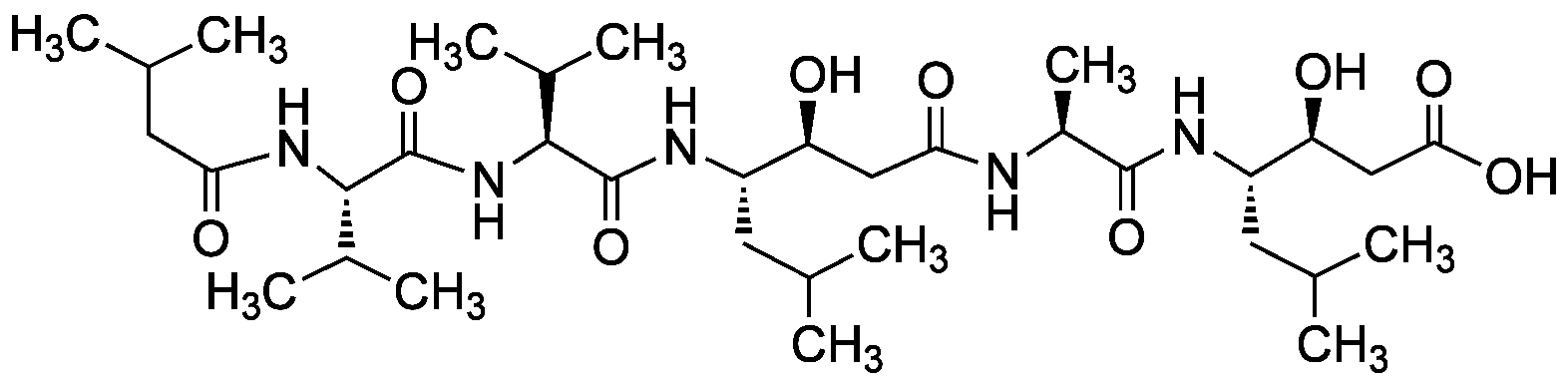
- SMILESCC(C)C[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)C[C@H](O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)CC(C)C)C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Pepstatin, a new pepsin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes: H. Umezawa, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 23, 259 (1970)
- Inhibition of cathepsin D-type proteinase of macrophages by pepstatin, a specific pepsin inhibitor, and other substances: M.H. McAdoo, et al.; Infect. Immun. 7, 655 (1973)
- Mode of inhibition of acid proteases by pepstatin: J. Jr. Marciniszyn, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 251, 7088 (1976)
- Non-specific inhibition of pressor agents in vivo by the renin inhibitor pepstatin A: A.A. Oldham, et al.; J. Hypertens. 2, 157 (1984)
- Inhibition of aspartic proteases by pepstatin and 3-methylstatine derivatives of pepstatin. Evidence for collected-substrate enzyme inhibition: D.H. Rich, et al.; Biochemistry 24, 3165 (1985)
- Inhibition of HIV replication in cell culture by the specific aspartic protease inhibitor pepstatin A: K. von der Helm, et al.; FEBS Lett. 247, 349 (1989)
- Cathepsin D protease mediates programmed cell death induced by interferon-gamma, Fas/APO-1 and TNF-alpha: L.P. Deiss, et al.; EMBO J. 15, 3861 (1996)
- Pepstatin A-sensitive aspartic proteases in lysosome are involved in degradation of the invariant chain and antigen-processing in antigen presenting cells of mice infected with Leishmania major: T. Zhang, et al.; BBRC 276, 693 (2000)
- Linear non-competitive inhibition of solubilized human gamma-secretase by pepstatin A methylester, L685458, sulfonamides, and benzodiazepines: G. Tian, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 31499 (2002)
- Pepstatin A, an aspartic proteinase inhibitor, suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation: H. Yoshida, et al.; J. Biochem. 139, 583 (2006)
