WB analysis of PGCB recombinant protein using GTX14784 PGCB antibody. Dilution : 1:500
PGCB antibody
GTX14784
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetNPR2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NamePGCB antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
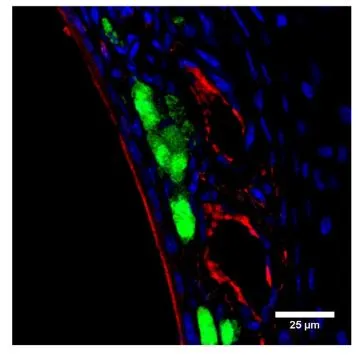
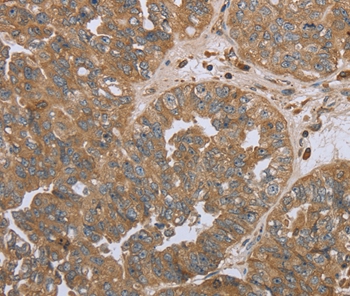
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500. ICC/IF: 1:200. IP: 1:200. ELISA: 1:10000. IHC: 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.75-1.20 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID4882
- Target nameNPR2
- Target descriptionnatriuretic peptide receptor 2
- Target synonymsAMD1, AMDM, ANPRB, ANPb, ECDM, GC-B, GCB, GUC2B, GUCY2B, NPRB, NPRBi, SNSK, atrial natriuretic peptide receptor 2, atrial natriuretic peptide B-type receptor, atrial natriuretic peptide receptor type B, guanylate cyclase 2B, guanylate cyclase B, guanylyl cyclase B, natriuretic peptide receptor B/guanylate cyclase B (atrionatriuretic peptide receptor B)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP20594
- Protein NameAtrial natriuretic peptide receptor 2
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes natriuretic peptide receptor B, one of two integral membrane receptors for natriuretic peptides. Both NPR1 and NPR2 contain five functional domains: an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a single membrane-spanning region, and intracellularly a protein kinase homology domain, a helical hinge region involved in oligomerization, and a carboxyl-terminal guanylyl cyclase catalytic domain. The protein is the primary receptor for C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP), which upon ligand binding exhibits greatly increased guanylyl cyclase activity. Mutations in this gene are the cause of acromesomelic dysplasia Maroteaux type. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203