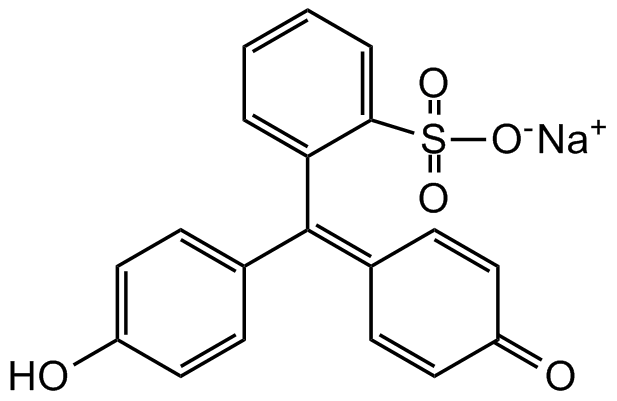
Chemical Structure
Phenol red sodium salt [34487-61-1] [34487-61-1]
CDX-P0026
CAS Number34487-61-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity0.9
Molecular Weight376.36
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NamePhenol red sodium salt [34487-61-1] [34487-61-1]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number34487-61-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity0.9
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC19H13O5S . Na
- Molecular Weight376.36
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 34487-61-1. Formula: C19H13O5S . Na. MW: 376.36. Synthetic Water soluble pH indicator used in the 6.8 (yellow) to 8.2 (red) range and frequently used in cell biology laboratories. Widely used as cell tissue culture pH marker. A small amount of phenol red added to the growth medium will have a pink-red color under normal conditions. Typically, 15 mg/l are used for cell culture. In the event of problems, waste products produced by dying cells or overgrowth of contaminants will cause a change in pH, leading to a change in indicator color. For example, a culture of relatively slowly dividing mammalian cells can be quickly overgrown by bacterial contamination. This usually results in an acidification of the medium, turning it yellow. The waste products produced by the mammalian cells themselves will slowly decrease the pH, gradually turning the solution orange and then yellow. This color change is an indication that even in the absence of contamination, the medium needs to be replaced. Shown to be a weak estrogen mimic (possible through inpurities), which can enhance the growth of cells that express the estrogen receptor in cell cultures. Might be useful as a differentiation factor. - Water soluble pH indicator used in the 6.8 (yellow) to 8.2 (red) range and frequently used in cell biology laboratories. Widely used as cell tissue culture pH marker. A small amount of phenol red added to the growth medium will have a pink-red color under normal conditions. Typically, 15 mg/l are used for cell culture. In the event of problems, waste products produced by dying cells or overgrowth of contaminants will cause a change in pH, leading to a change in indicator color. For example, a culture of relatively slowly dividing mammalian cells can be quickly overgrown by bacterial contamination. This usually results in an acidification of the medium, turning it yellow. The waste products produced by the mammalian cells themselves will slowly decrease the pH, gradually turning the solution orange and then yellow. This color change is an indication that even in the absence of contamination, the medium needs to be replaced. Shown to be a weak estrogen mimic (possible through inpurities), which can enhance the growth of cells that express the estrogen receptor in cell cultures. Might be useful as a differentiation factor.
- SMILES[Na+].OC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=C1C=CC(=O)C=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1S([O-])(=O)=O
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12352200

![Phenol Red sodium salt [34487-61-1] [34487-61-1]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/12/D5/CgoaEGZGsG6EB4NFAAAAAH3ZqXg099.jpg)