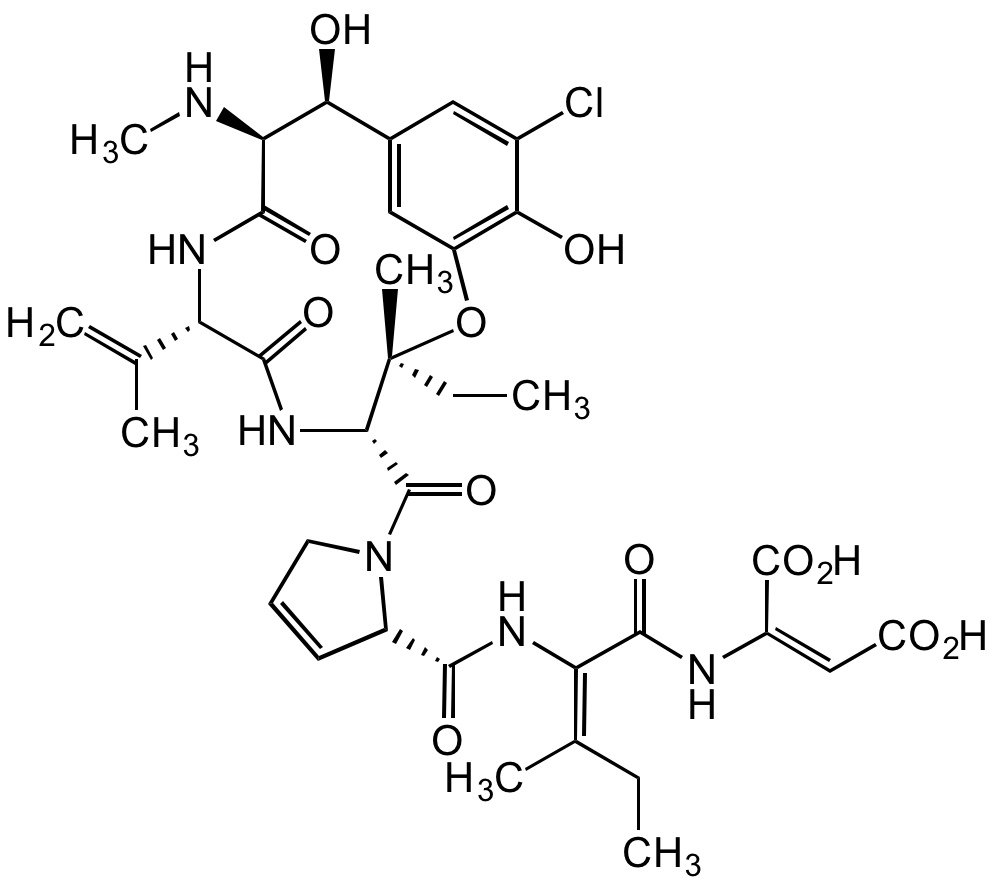
Chemical Structure
Phomopsin A [64925-80-0]

AG-CN2-0515
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NamePhomopsin A [64925-80-0]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number64925-80-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC36H45ClN6O12
- Molecular Weight789.2
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 64925-80-0. Formula: C36H45ClN6O12. MW: 789.2. Isolated from Phomopsis leptostromiformis. Macrocyclic heptapeptide mycotoxin. Potent anti-mitotic compound that can cause cell death. Microtubule assembly inhibitor. Binds selectively to dimeric tubulin, inhibiting the formation of the microtubule spindle to block cell division. Binds at a site different from the colchicine binding site and overlapping the vinblastine binding site. Inhibits tubulin-dependent GTP hydrolysis. Binds beta-tubulin from higher organisms but not alpha-tubulin or fungal mycelial tubulin. Causes lupinosis (a degenerative disorder) in livestock fed infected lupins. - Macrocyclic heptapeptide mycotoxin. Potent anti-mitotic compound that can cause cell death. Microtubule assembly inhibitor. Binds selectively to dimeric tubulin, inhibiting the formation of the microtubule spindle to block cell division. Binds at a site different from the colchicine binding site and overlapping the vinblastine binding site. Inhibits tubulin-dependent GTP hydrolysis. Binds beta-tubulin from higher organisms but not alpha-tubulin or fungal mycelial tubulin. Causes lupinosis (a degenerative disorder) in livestock fed infected lupins.
- SMILESClC1=CC([C@H](O)[C@@H]2NC)=CC(O[C@@](C)(CC)[C@H](C(N3CC=C[C@H]3C(N/C(C(N/C(C(O)=O)=C/C(O)=O)=O)=C(C)/CC)=O)=O)NC([C@H](C(C)=C)NC2=O)=O)=C1O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Interaction of phomopsin A and related compounds with purified sheep brain tubulin: E. Lacey, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 2133 (1987)
- Effect of phomopsin A on the alkylation of tubulin: R.F. Luduena, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 39, 1603 (1990)
- Dolastatin 10, a powerful cytostatic peptide derived from a marine animal. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization mediated through the vinca alkaloid binding domain: R. Bai, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 39, 1941 (1990)
- Binding selectivity of rhizoxin, phomopsin A, vinblastine, and ansamitocin P-3 to fungal tubulins: differential interactions of these antimitotic agents with brain and fungal tubulins: Y. Li, et al.; BBRC 187, 722 (1992)
- Interaction of phomopsin A with porcine brain tubulin. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization and binding at a rhizoxin binding site: Y. Li, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 43, 219 (1992)
- Natural products which interact with tubulin in the vinca domain: maytansine, rhizoxin, phomopsin A, dolastatins 10 and 15 and halichondrin B: E. Hamel; Pharmacol. Ther. 55, 31 (1992)
- Interaction of phomopsin A with normal and subtilisin-treated bovine brain tubulin: A.R. Chaudhuri & R.F. Luduena; J. Protein Chem. 16, 99 (1997)
- Localization of the antimitotic peptide and depsipeptide binding site on beta-tubulin: A. Mitra & D. Sept; Biochemistry 43, 13955 (2004)
- Structural insight into the inhibition of tubulin by vinca domain peptide ligands: A. Cormier, et al.; EMBO Rep. 9, 1101 (2008)
