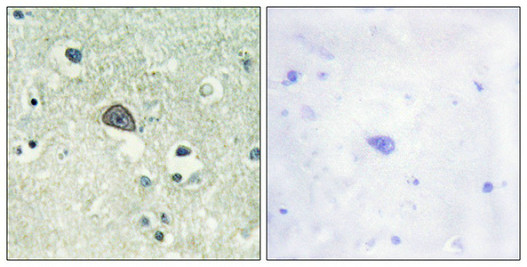
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue using NMDAR1 (Phospho-Ser890) antibody (left)or the same antibody preincubated with blocking peptide (right).
Phospho-GRIN1 (Ser890) Antibody
CSB-PA126380
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetGRIN1
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NamePhospho-GRIN1 (Ser890) Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2902
- Target nameGRIN1
- Target descriptionglutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 1
- Target synonymsGluN1; glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit zeta-1; glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1; glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 1; MRD8; NDHMSD; NDHMSR; NMDA1; NMDAR1; NMD-R1; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel, subunit zeta-1; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR1; NR1; putative NMDtranscript(altAcc_e2)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ05586
- Protein NameGlutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1
- Scientific DescriptionNMDA receptors are members of the ionotropic class of glutamate receptors, which also includes Kainate and AMPA receptors. NMDA receptors consist of NR1 subunits combined with one or more NR2 (A-D) or NR3 (A-B) subunits. The ligand-gated channel is permeable to cations including Ca2+, and at resting membrane potentials NMDA receptors are inactive due to a voltage-dependent blockade of the channel pore by Mg2+. NMDA receptor activation, which requires binding of glutamate and glycine, leads to an influx of Ca2+ into the postsynaptic region where it activates several signaling cascades, including pathways leading to the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD). NMDA receptors have a critical role in excitatory synaptic transmission and plasticity in the CNS. They govern a range of physiological conditions including neurological disorders caused by excitotoxic neuronal injury, psychiatric disorders and neuropathic pain syndromes. Guang Bai, J. Biol. Chem., Jan 1998; 273: 1086. Guang Bai, J. Biol. Chem., Mar 1995; 270: 7737. Mai T. Dang, PNAS, Oct 2006; 103: 15254 - 15259.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC12352203