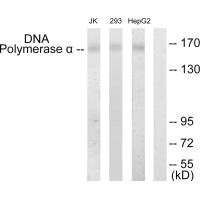
Western blot analysis of extracts from Jurkat cells, 293 cells and HepG2 cells, using DNA Polymerase alpha antibody.
POLA1 Antibody
CSB-PA156369
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetPOLA1
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NamePOLA1 Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID5422
- Target namePOLA1
- Target descriptionDNA polymerase alpha 1, catalytic subunit
- Target synonymsNSX, PDR, POLA, VEODS, p180, DNA polymerase alpha catalytic subunit, DNA polymerase alpha catalytic subunit p180, polymerase (DNA directed), alpha 1, catalytic subunit, polymerase (DNA) alpha 1, catalytic subunit, polymerase (DNA-directed), alpha (70kD)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP09884
- Protein NameDNA polymerase alpha catalytic subunit
- Scientific DescriptionPlays an essential role in the initiation of DNA replication. During the S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA polymerase alpha complex (composed of a catalytic subunit POLA1/p180, a regulatory subunit POLA2/p70 and two primase subunits PRIM1/p49 and PRIM2/p58) is recruited to DNA at the replicative forks via direct interactions with MCM10 and WDHD1. The primase subunit of the polymerase alpha complex initiates DNA synthesis by oligomerising short RNA primers on both leading and lagging strands. These primers are initially extended by the polymerase alpha catalytic subunit and subsequently transferred to polymerase delta and polymerase epsilon for processive synthesis on the lagging and leading strand, respectively. The reason this transfer occurs is because the polymerase alpha has limited processivity and lacks intrinsic 3 exonuclease activity for proofreading error, and therefore is not well suited for replicating long complexes. Wong S.W., EMBO J. 7:37-47(1988). Pearson B.E., Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:2081-2095(1991). Hsi K.-L., Nucleic Acids Res. 18:6231-6237(1990).
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC41116161







