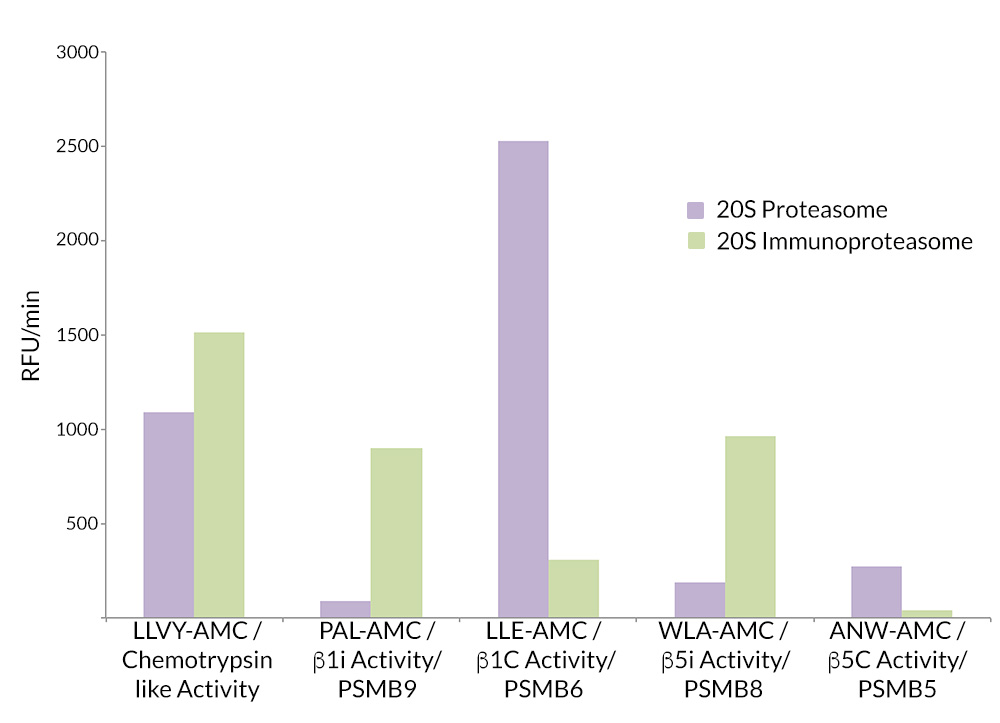
20S Immunoproteasome vs. 20S Constitutive Proteasome Activity: 20S Proteasome is most active against Suc-LLVY-AMC (SBB-PS0010), Ac-LLE-AMC (SBB-PS0006), and Ac-WLA-AMC (SBB-PS0008) substrates, representing physiologically relevant chymotrypsin-like, beta1c, and beta5c proteasome activity respectively.
20S Proteasome (human) (untagged)

SBB-PP0005
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierSouth Bay Bio
- Product Name20S Proteasome (human) (untagged)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Scientific DescriptionProtein. Human 20S Proteasome. Source: Human Erythrocytes. Formulation: Liquid. In 50mM HEPES pH 7.6, 100mM sodium chloride, 1mM DTT. Purity: >95% (SDS-PAGE). The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is the major proteolytic system in eukaryotic cells, where it catalyzes the selective degradation of short-lived regulatory proteins or the rapid turnover of misfolded proteins. One of the most important proteases in this pathway is the 26S proteasome, an ATP-dependent proteolytic complex, which is formed by the association of the barrel-shaped 20S proteasome (700kDa) and two 19S (700kDa) regulatory complexes. The 20S catalytic core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha-subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta-subunits. The 20S catalytic core is able to degrade a variety of peptide substrates and poly-ubiquitinated proteins involved with apoptosis, DNA repair, endocytosis and cell cycle control. - The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is the major proteolytic system in eukaryotic cells, where it catalyzes the selective degradation of short-lived regulatory proteins or the rapid turnover of misfolded proteins. One of the most important proteases in this pathway is the 26S proteasome, an ATP-dependent proteolytic complex, which is formed by the association of the barrel-shaped 20S proteasome (700kDa) and two 19S (700kDa) regulatory complexes. The 20S catalytic core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha-subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta-subunits. The 20S catalytic core is able to degrade a variety of peptide substrates and poly-ubiquitinated proteins involved with apoptosis, DNA repair, endocytosis and cell cycle control.
- Storage Instruction-80°C
- UNSPSC12352202
