Chemical Structure
Pyripyropene A [147444-03-9]

AG-CN2-0106
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NamePyripyropene A [147444-03-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number147444-03-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Hazard InformationWarning
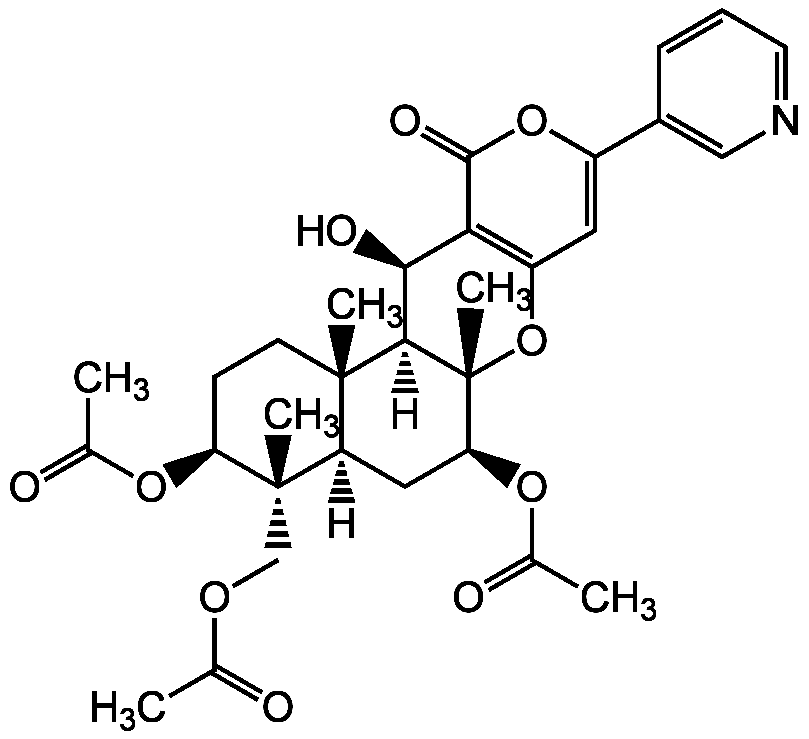
- Molecular FormulaC31H37NO10
- Molecular Weight583.6
- Scientific DescriptionAntibiotic [1]. Highly specific inhibitor of acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acetyltransferase 2 (ACAT2) [1-6, 8, 9]. Anti-angiogenic [10]. Antiatherogenic and antiatherosclerotic agent. Shows cholesterol-lowering and atheroprotective activities. [7, 11, 12]. - Chemical. CAS: 147444-03-9. Formula: C31H37NO10. MW: 583.6. Isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus FO-1289. Antibiotic. Highly specific inhibitor of acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acetyltransferase 2 (ACAT2). Anti-angiogenic. Antiatherogenic and antiatherosclerotic agent. Shows cholesterol-lowering and atheroprotective activities.
- SMILES[H][C@@]12C[C@H](OC(C)=O)[C@@]3(C)OC4=C([C@H](O)[C@]3([H])[C@@]1(C)CC[C@H](OC(C)=O)C2(C)COC(C)=O)C(=O)OC(=C4)C1=CN=CC=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Pyripyropenes, highly potent inhibitors of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase produced by Aspergillus fumigatus: S. Omura, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 46, 1168 (1993)
- Pyripyropenes, novel inhibitors of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. II. Structure elucidation of pyripyropenes A, B, C and D: Y.K. Kim, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 47, 154 (1994)
- Pyripyropenes, novel inhibitors of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. I. Production, isolation, and biological properties: H. Tomoda, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 47, 148 (1994)
- Mass-production of human ACAT-1 and ACAT-2 to screen isoform-specific inhibitor: a different substrate specificity and inhibitory regulation: K.H. Cho, et al.; BBRC 309, 864 (2003)
- Identification of ACAT1- and ACAT2-specific inhibitors using a novel, cell-based fluorescence assay: individual ACAT uniqueness: A.T. Lada, et al.; J. Lipid Res. 45, 378 (2004)
- Selectivity of microbial acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitors toward isozymes: T. Ohshiro, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 60, 43 (2007)
- Potential therapeutics for obesity and atherosclerosis: inhibitors of neutral lipid metabolism from microorganisms: H. Tomoda & S. Omura; Pharmacol. Ther. 115, 375 (2007) (Review)
- Identification of the interaction site within acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase 2 for the isoform-specific inhibitor pyripyropene A: A. Das, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 283, 10453 (2008)
- Selectivity of pyripyropene derivatives in inhibition toward acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase 2 isozyme: T. Ohshiro, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo). 61, 503 (2008)
- Pyripyropenes, fungal sesquiterpenes conjugated with alpha-pyrone and pyridine moieties, exhibits anti-angiogenic activity against human umbilical vein endothelial cells: A. Hayashi, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 32, 1261 (2009)
