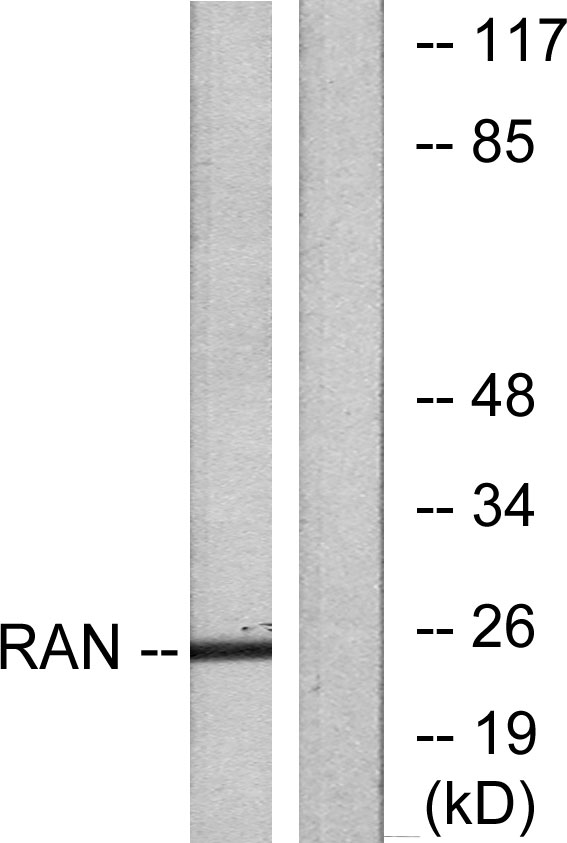
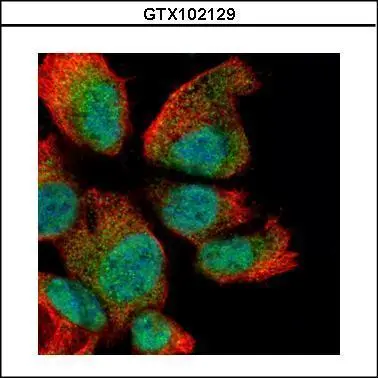
RAN antibody
GTX80345
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityYeast
TargetRAN
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameRAN antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteRecommended Starting Dilutions:Use at 1:1000Optimal dilutions should be determined experimentally by the researcher.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID5901
- Target nameRAN
- Target descriptionRAN, member RAS oncogene family
- Target synonymsARA24, Gsp1, TC4, GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran, GTPase Ran, RanGTPase, androgen receptor-associated protein 24, guanosine triphosphatase Ran, member RAS oncogene family, ras-like protein TC4, ras-related nuclear protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP62826
- Protein NameGTP-binding nuclear protein Ran
- Scientific DescriptionRAN (ras-related nuclear protein) is a small GTP binding protein belonging to the RAS superfamily that is essential for the translocation of RNA and proteins through the nuclear pore complex. The RAN protein is also involved in control of DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression. Nuclear localization of RAN requires the presence of regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1). Mutations in RAN disrupt DNA synthesis. Because of its many functions, it is likely that RAN interacts with several other proteins. RAN regulates formation and organization of the microtubule network independently of its role in the nucleus-cytosol exchange of macromolecules. RAN could be a key signaling molecule regulating microtubule polymerization during mitosis. RCC1 generates a high local concentration of RAN-GTP around chromatin which, in turn, induces the local nucleation of microtubules. RAN is an androgen receptor (AR) coactivator that binds differentially with different lengths of polyglutamine within the androgen receptor. Polyglutamine repeat expansion in the AR is linked to Kennedys disease (X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy). RAN coactivation of the AR diminishes with polyglutamine expansion within the AR, and this weak coactivation may lead to partial androgen insensitivity during the development of Kennedys disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityYeast
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Karyopherin Kap114p-mediated trans-repression controls ribosomal gene expression under saline stress. Liao CC et al., 2020 Jul 3, EMBO RepRead this paper