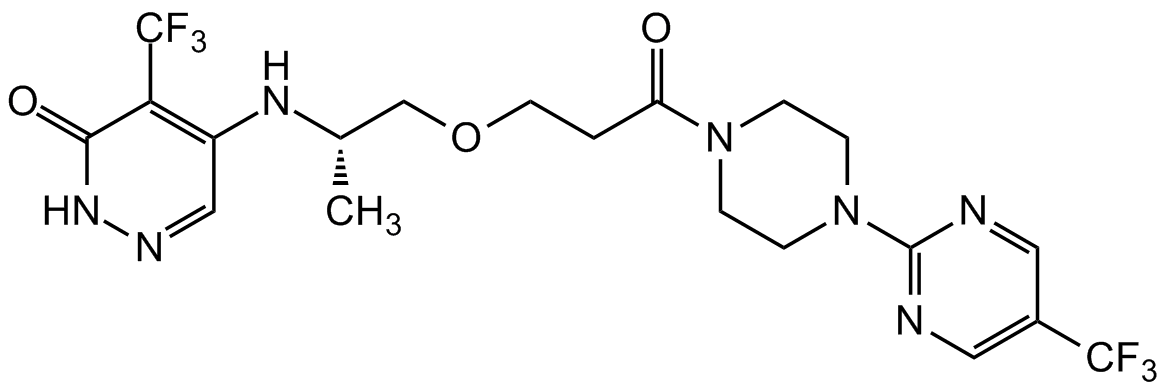
Chemical Structure
RBN-2397 [2381037-82-5]

AG-CR1-3547
CAS Number2381037-82-5
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight523.4
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameRBN-2397 [2381037-82-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number2381037-82-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC20H23F6N7O3
- Molecular Weight523.4
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 2381037-82-5. Formula: C20H23F6N7O3. MW: 523.4. RBN-2397 is a potent NAD+ competitive small molecule inhibitor of PARP-7. RBN-2397 selectively inhibits PARP-7 and demonstrates >50-fold selectivity for inhibition of PARP-7 over all PARP family members as measured by biochemical assays. RBN-2397 inhibits PARP-7-dependent MARylation (IC50 = 2nM) in cell biochemical assay and inhibits cells proliferation in NCI-H1373 lung cancer cells (IC50 = 20nM). By selectively inhibiting PARP-7 in tumor cells, RBN-2397 has been shown to directly inhibit cellular proliferation and restore Type I interferon signaling to stimulate an innate and adaptive antitumor immune response. Targeting cytosolic nucleic acid sensing pathways and the Type I interferon (IFN) response is an emerging therapeutic strategy being explored in oncology. The PARP family consists of seventeen enzymes that regulate fundamental biological processes including response to cellular stress. Normal cells do not express high levels of PARP-7. PARP-7 is upregulated in response to cellular stress, including exposure to toxins in cigarette smoke, steroid hormones and during viral infection. PARP-7 (TIPARP) is a monoPARP that catalyzes the transfer of single units of ADP-ribose onto substrates (MARylation) to change their function and plays a role in suppressing the Type I IFN response. PARP-7 serves as a brake in cancer cells to block the production of Type I interferons and suppress the normal cellular stress response. Thus, the expression of PARP-7 enables cancer cells to escape senescence or the loss of a cells ability to divide and avoid immune detection and subsequent elimination. - RBN-2397 is a potent NAD+ competitive small molecule inhibitor of PARP-7. RBN-2397 selectively inhibits PARP-7 and demonstrates >50-fold selectivity for inhibition of PARP-7 over all PARP family members as measured by biochemical assays. RBN-2397 inhibits PARP-7-dependent MARylation (IC50 = 2nM) in cell biochemical assay and inhibits cells proliferation in NCI-H1373 lung cancer cells (IC50 = 20nM). By selectively inhibiting PARP-7 in tumor cells, RBN-2397 has been shown to directly inhibit cellular proliferation and restore Type I interferon signaling to stimulate an innate and adaptive antitumor immune response. Targeting cytosolic nucleic acid sensing pathways and the Type I interferon (IFN) response is an emerging therapeutic strategy being explored in oncology. The PARP family consists of seventeen enzymes that regulate fundamental biological processes including response to cellular stress. Normal cells do not express high levels of PARP-7. PARP-7 is upregulated in response to cellular stress, including exposure to toxins in cigarette smoke, steroid hormones and during viral infection. PARP-7 (TIPARP) is a monoPARP that catalyzes the transfer of single units of ADP-ribose onto substrates (MARylation) to change their function and plays a role in suppressing the Type I IFN response. PARP-7 serves as a brake in cancer cells to block the production of Type I interferons and suppress the normal cellular stress response. Thus, the expression of PARP-7 enables cancer cells to escape senescence or the loss of a cells ability to divide and avoid immune detection and subsequent elimination.
- SMILESO=C1NN=CC(N[C@@H](C)COCCC(N2CCN(C3=NC=C(C(F)(F)F)C=N3)CC2)=O)=C1C(F)(F)F
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
