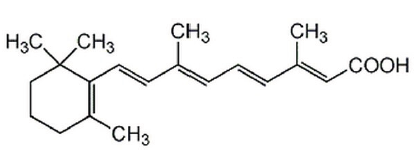
Chemical Structure
Retinoic Acid Sterile Solution
IAX-700-109
Estimated Purity>95%
Product group Chemicals
Molecular Weight300.44
Overview
- SupplierInnaxon
- Product NameRetinoic Acid Sterile Solution
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC20H28O2
- Molecular Weight300.44
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 302-79-4. Formula: C20H28O2. MW: 300.44. Soluble in water, PBS, Tris and other physiological solutions as formulated in a proprietary, thermostable, aqueous lipid nanoparticulate formulation (Lipodisq). Vitamin A is a fat-soluble micronutrient necessary for the growth of healthy skin and hair. However, both too little and too much vitamin A has deleterious effects. All-transretinoic acid (ATRA) and retinal are the main active metabolites of vitamin A. Retinoic acid dose-dependently regulates hair follicle stem cells, influencing the functioning of the hair cycle, wound healing, and melanocyte stem cells. Retinoic acid also influences melanocyte differentiation and proliferation in a dose-dependent and temporal manner. Levels of retinoids decline when exposed to ultraviolet irradiation in the skin. All-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) is effective for preventing cancer and treating skin diseases and acute promyelocytic leukaemia (APL). These pharmacological effects of ATRA are mainly mediated by retinoid X receptors (RXRs) and retinoic acid receptors (RARs). These included two families of receptors, the RAR isotypes (a,b, and g) along with three RXR isotypes (a,b, and g), which bind as RXR/RAR heterodimers to cis-acting response elements of RA target genes to generate a high degree of complexity. Retinoic acid is used in the treatment of psoriasis, ichthyosis, follicular keratosis, acne, lichen planus, verrucous epidermal nevus, impetigo, vitiligo, lichen psoriasis, the face of pityriasis alba. - Vitamin A is a fat-soluble micronutrient necessary for the growth of healthy skin and hair. However, both too little and too much vitamin A has deleterious effects. All-transretinoic acid (ATRA) and retinal are the main active metabolites of vitamin A. Retinoic acid dose-dependently regulates hair follicle stem cells, influencing the functioning of the hair cycle, wound healing, and melanocyte stem cells. Retinoic acid also influences melanocyte differentiation and proliferation in a dose-dependent and temporal manner. Levels of retinoids decline when exposed to ultraviolet irradiation in the skin. All-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) is effective for preventing cancer and treating skin diseases and acute promyelocytic leukaemia (APL). These pharmacological effects of ATRA are mainly mediated by retinoid X receptors (RXRs) and retinoic acid receptors (RARs). These included two families of receptors, the RAR isotypes (a,b, and g) along with three RXR isotypes (a,b, and g), which bind as RXR/RAR heterodimers to cis-acting response elements of RA target genes to generate a high degree of complexity. Retinoic acid is used in the treatment of psoriasis, ichthyosis, follicular keratosis, acne, lichen planus, verrucous epidermal nevus, impetigo, vitiligo, lichen psoriasis, the face of pityriasis alba.
- SMILESCC1(C)C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(O)=O)=C(C)CCC1
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
