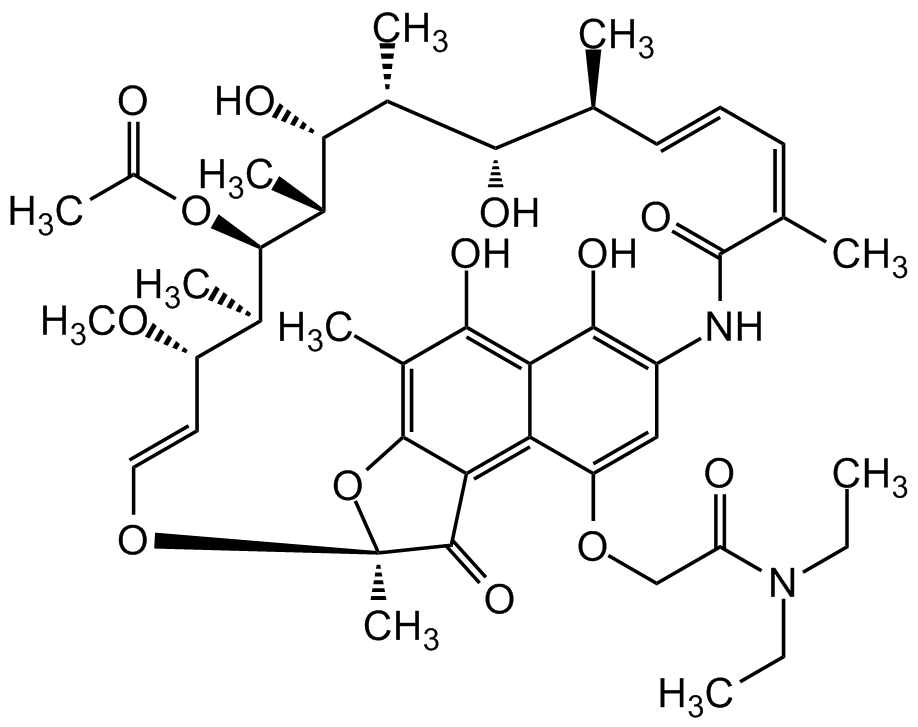
Chemical Structure
Rifamycin M14 [2750-76-7]

AG-CN2-0332
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameRifamycin M14 [2750-76-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number2750-76-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC43H58N2O13
- Molecular Weight810.9
- Scientific DescriptionAnsamycin antibiotic. Selective inhibitor of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RNAP). Effective against mycobacteria and therefore used in research of tuberculosis, leprosy and Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections. - Chemical. CAS: 2750-76-7. Formula: C43H58N2O13. MW: 810.9. Semisynthetic. Ansamycin antibiotic. Selective inhibitor of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RNAP). Effective against mycobacteria, and are therefore used in research of tuberculosis, leprosy and mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections.
- SMILESOC1=C(NC(/C(C)=C\C=C\[C@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](C)[C@H]([C@@H](C)[C@@H]([C@H](C)[C@H](/C=C/O2)OC)OC(C)=O)O)=O)C=C(OCC(N(CC)CC)=O)C3=C4C(O[C@@]2(C)C4=O)=C(C)C(O)=C31
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC51280000
References
- In vitro bacteriological studies on rifamycin B diethylamide (rifamide): R. Pallanza, et al.; Arzneimittelforschung 15, 800 (1965)
- The inhibition of bacterial RNA synthesis by the rifamycin antibiotics: J.M. Wilhelm, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 166, 268 (1968)
- Rifamycins: A General View: S. Riva & L.G. Silvestri; Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 26, 199 (1972)
- Rifamycin antibiotics: inhibitors of Rauscher murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase and of purified DNA polymerases from human normal and leukemic lymphoblasts: S.S. Yang, et al.; J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 49, 7 (1972)
- Rifamycin Derivatives Strongly Inhibiting RNA>DNA Polymerase (Reverse Transcriptase) of Murine Sarcoma Viruses: C. Gurgo, et al.; J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 49, 61 (1972)
- Inhibition of poly(A) polymerase by rifamycin derivatives: S.T. Jacob & K.M. Rose; Nucl. Acids Res. 1, 1549 (1974)
- Structure-Activity Relationships and DNA Polymerases From Normal and Specificity of Inhibition of Leukemia Cells of Man and From Simian Sarcoma Virus by Rifamycin Derivatives: R.A. CiCioccio & B.I.S. Srivastava; J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 61, 1187 (1978)
- Comparison of antibacterial and antiimmune effects of certain rifamycins: J.E. Kasik & M. Monick; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 19, 134 (1981)
- In vitro activity of rifamycins alone and in combination with other antibiotics against Chlamydia trachomatis: R.B. Jones, et al.; Rev. Infect. Dis. 5, S556 (1983)
- QSAR Modeling of Antimycobacterial Activity and Activity Against Other Bacteria of 3-Formyl Rifamycin SV Derivatives: D. Dimov, et al.; Quant. Struct.-Act. Relat. 20, 298 (2001)
