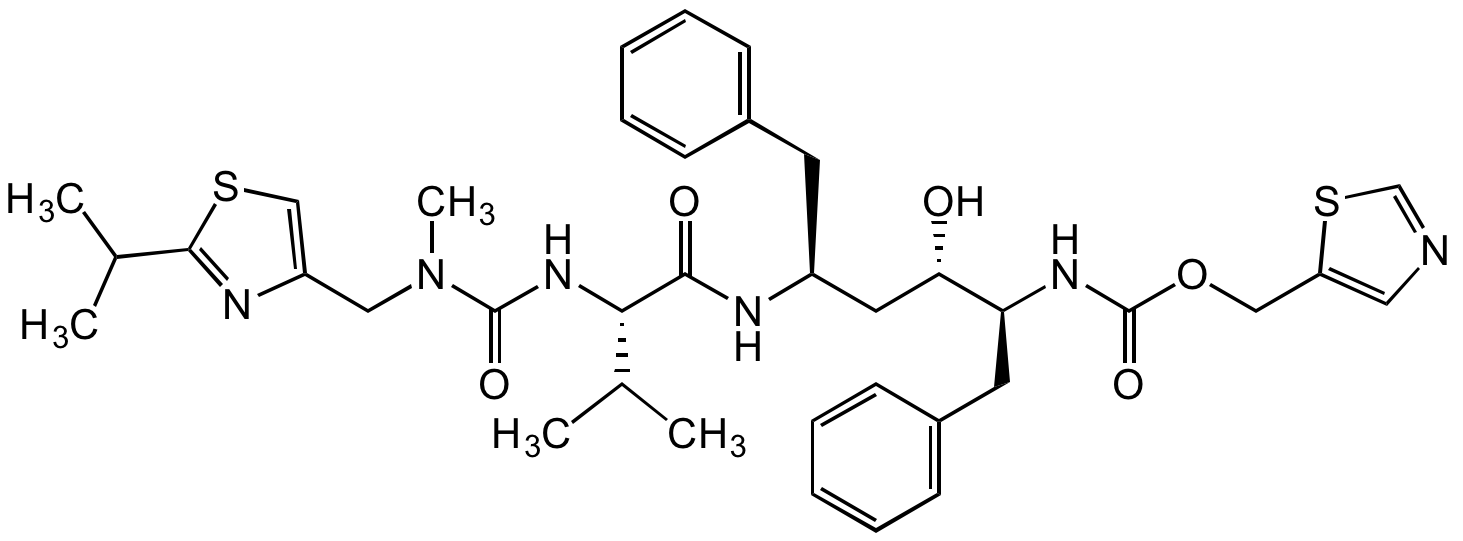
Chemical Structure
Ritonavir [155213-67-5]

AG-CR1-3683
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameRitonavir [155213-67-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number155213-67-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC37H48N6O5S2
- Molecular Weight720.9
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 155213-67-5. Formula: C37H48N6O5S2. MW: 720.9. . HIV-1 and HIV-2 protease inhibitor. Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) and 4 (GLUT4) inhibitor. Inhibits transport of glucose across the plasma membranes of mammalian cells and consequently decreases glycolysis. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Antitumor agent. Apoptosis inducer and cell proliferation inhibitor in GLUT1/GLUT4 overexpressed cancer cell lines. Tumor cells rely on elevated glucose consumption and metabolism for survival and proliferation. Glucose transporters mediating glucose entry are key proximal rate-limiting checkpoints. Among the fourteen SLC2A family members, GLUTs 1 and 4 are high-affinity glucose transporters. - HIV-1 and HIV-2 protease inhibitor. Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) and 4 (GLUT4) inhibitor. Inhibits transport of glucose across the plasma membranes of mammalian cells and consequently decreases glycolysis. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Antitumor agent. Apoptosis inducer and cell proliferation inhibitor in GLUT1/GLUT4 overexpressed cancer cell lines. Tumor cells rely on elevated glucose consumption and metabolism for survival and proliferation. Glucose transporters mediating glucose entry are key proximal rate-limiting checkpoints. Among the fourteen SLC2A family members, GLUTs 1 and 4 are high-affinity glucose transporters. Inhibits 20S proteasome chymotrypsin-like activity. The proteinase inhibitor Kaletra, which is a mixture of the HIV-1 proteinase inhibitors lopinavir and ritonavir has been shown to be effective against SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. Shown in a SARS-CoV-2 protease structure model study to potentially bind and inhibit the coronavirus endopeptidase C30 (CEP_C30) of SARS-CoV-2. An initial randomized trial study was not successful.
- SMILESCC(C1=NC(CN(C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C[C@@H]([C@@H](NC(OCC2=CN=CS2)=O)CC3=CC=CC=C3)O)CC4=CC=CC=C4)=O)C(C)C)=O)C)=CS1)C
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- ABT-538 is a potent inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus protease and has high oral bioavailability in humans: D.J. Kempf, et al.; PNAS 92, 2484 (1995)
- Discovery of ritonavir, a potent inhibitor of HIV protease with high oral bioavailability and clinical efficacy: D.J. Kempf, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 41, 602 (1998)
- Pharmacological and therapeutic properties of ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor therapy in HIV-infected patients: R.K. Zeldin, et al.; J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 53, 4 (2004)
- HIV protease inhibitors act as competitive inhibitors of the cytoplasmic glucose binding site of GLUTs with differing affinities for GLUT1 and GLUT4: R.C. Hresko & P.W. Hruz; PLoS One 6, e25237 (2011)
- Targeting Glycolysis and Compensatory Mitochondrial Metabolism In An In Vivo Xenograft Model Of Multiple Myeloma With FDA Approved Ritonavir and Metformin: S. Dalva-Aydemir, et al.; Blood 122, 1922 (2013)
- Glucose transporter 1-mediated glucose uptake is limiting for B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia anabolic metabolism and resistance to apoptosis: T. Liu, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 5, e1470 (2014)
- In Silico Modeling-based Identification of Glucose Transporter 4 (GLUT4)-selective Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy: R.K. Mishra, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 290, 14441 (2015)
- A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists: L.A. O'Neill, et al.; Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 553 (2016)
- Development of GLUT4-selective antagonists for multiple myeloma therapy: C. Wei, et al.; Eur. J. Med. Chem. 139, 573 (2017)
