Chemical Structure
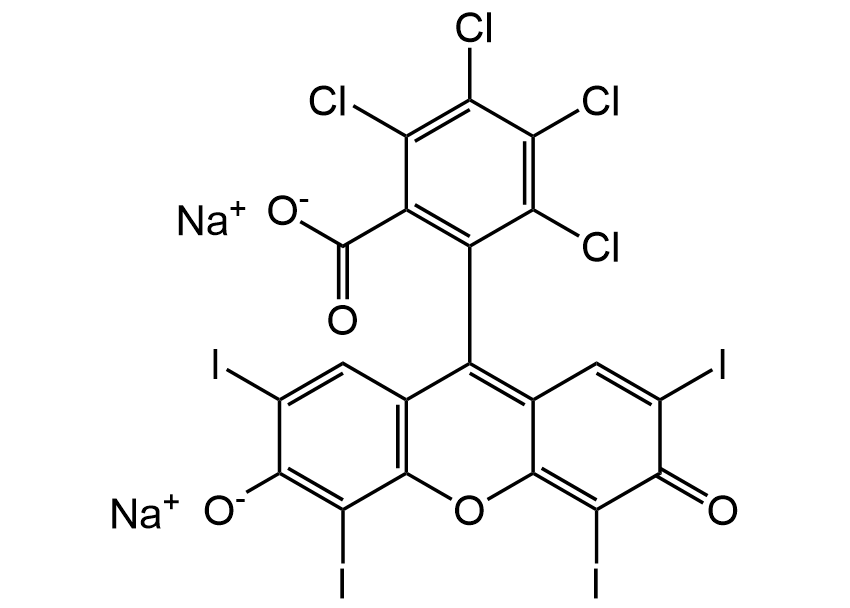
Rose Bengal sodium salt [632-69-9] [632-69-9]
CDX-R0132
CAS Number632-69-9
Product group Chemicals
Molecular Weight1017.64
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameRose Bengal sodium salt [632-69-9] [632-69-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number632-69-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Molecular FormulaC20H2Cl4I4O5 . 2Na
- Molecular Weight1017.64
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 632-69-9. Formula: C20H2Cl4I4O5 . 2Na. MW: 1017.64. Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml). Slightly soluble in water (1mg/ml). Rose Bengal is a xanthene dye, fluorescein derivative, and photosensitizer. In ophthalmology, Rose Bengal is used as a diagnostic stain to identify damaged or diseased cells in the eye. It helps in the diagnosis of dry eye syndrome and other ocular surface disorders. Rose Bengal is used in Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for treating certain types of cancers and other medical conditions. When exposed to light, Rose Bengal generates reactive oxygen species that can kill targeted cells. Rose Bengal is used to stain and differentiate various microorganisms and can be used as a tracer dye to study water movement and other environmental processes. Its spectral properties makes it useful for visual and fluorescence-based applications. Rose Bengal was originally used as a wool dye. Rose bengal inhibits the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP3A4/5 and the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) isoform UGT1A6 in human liver microsomes in a light-dependent manner. Rose Bengal is a potent VGlut and vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) inhibitor. High-purity form of Rose Bengal (>99.5% dye content) kills a battery of Gram-positive bacteria, including drug-resistant strains at low concentrations under fluorescent, LED, and natural light in a few minutes. Rose Bengal has been used for staining of live cells, but exhibits both intrinsic and phototoxicity. Spectral Data: lambdaex=548nm, lambdaem=567nm. - Rose Bengal is a xanthene dye, fluorescein derivative, and photosensitizer. In ophthalmology, Rose Bengal is used as a diagnostic stain to identify damaged or diseased cells in the eye. It helps in the diagnosis of dry eye syndrome and other ocular surface disorders. Rose Bengal is used in Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for treating certain types of cancers and other medical conditions. When exposed to light, Rose Bengal generates reactive oxygen species that can kill targeted cells. Rose Bengal is used to stain and differentiate various microorganisms and can be used as a tracer dye to study water movement and other environmental processes. Its spectral properties makes it useful for visual and fluorescence-based applications. Rose Bengal was originally used as a wool dye. Rose bengal inhibits the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP3A4/5 and the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) isoform UGT1A6 in human liver microsomes in a light-dependent manner. Rose Bengal is a potent VGlut and vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) inhibitor. High-purity form of Rose Bengal (>99.5% dye content) kills a battery of Gram-positive bacteria, including drug-resistant strains at low concentrations under fluorescent, LED, and natural light in a few minutes. Rose Bengal has been used for staining of live cells, but exhibits both intrinsic and phototoxicity. Spectral Data: lambdaex=548nm, lambdaem=567nm.
- SMILES[O-]C(c1c(C2=C3C=C(C(C(I)=C3Oc4c2cc(I)c([O-])c4I)=O)I)c(Cl)c(Cl)c(Cl)c1Cl)=O.[Na+].[Na+]
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12162000

![Rose Bengal sodium [632-69-9] [632-69-9]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/37/2C/CgoaEGaySQ-EZsLWAAAAAMNATh0487.png)