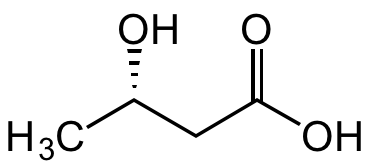
Chemical Structure
(S)-3-Hydroxybutyric acid [6168-83-8]

AG-CR1-3617
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Name(S)-3-Hydroxybutyric acid [6168-83-8]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number6168-83-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC4H8O3
- Molecular Weight104.1
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 6168-83-8. Formula: C4H8O3. MW: 104.1. Physiologically insignificant stereoisomer of (R)-3-Hydroxybutyric acid, a key metabolite of the ketolytic pathway. Anticonvulsant. Endogenous inhibitor of histone deacetylases (HDACs) 1, 3 and 4. Ligand of free fatty acid receptor 3 (FFAR3; GPR41) and hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCAR2; GPR109B). NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor. Prevents K+-efflux and reduces ASC oligomerization and speck formation. - Physiologically insignificant stereoisomer of (R)-3-Hydroxybutyric acid, a key metabolite of the ketolytic pathway. Anticonvulsant. Endogenous inhibitor of histone deacetylases (HDACs) 1, 3 and 4. Ligand of free fatty acid receptor 3 (FFAR3; GPR41) and hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCAR2; GPR109B). NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor. Prevents K+-efflux and reduces ASC oligomerization and speck formation.
- SMILESC[C@H](O)CC(O)=O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Effects of beta-hydroxy butyric acid on insulin binding to its receptor and on autophosphorylation of the receptor: H. Ohtusaka, et al.; Endocrinol. Jpn. 37, 915 (1990)
- Acetoacetate, acetone, and dibenzylamine (a contaminant in L-(+)-beta-hydroxybutyrate) exhibit direct anticonvulsant actions in vivo: J.M. Rho, et al.; Epilepsia 43, 358 (2002)
- The direct measurement of 3-beta-hydroxy butyrate enhances the management of diabetic ketoacidosis in children and reduces time and costs of treatment: M. Vanelli, et al.; Diabetes Nutr. Metab. 16, 312 (2003)
- Detection of cerebral {beta}-hydroxy butyrate, acetoacetate, and lactate on proton MR spectroscopy in children with diabetic ketoacidosis: S.L. Wootton-Gorges, et al.; AJNR 26, 1286 (2005)
- beta-Hydroxybutyrate activates the NF-kappaB signaling pathway to promote the expression of pro-inflammatory factors in calf hepatocytes: X. Shi, et al.; Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 33, 920 (2014)
- beta-hydroxybutyrate: Much more than a metabolite: J. C. Newman & E. Verdin; Diab. Res. Clin. Pract. 106, 173 (2014) (Review)
- BHBA suppresses LPS-induced inflammation in BV-2 cells by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation: S.P. Fu, et al.; Med. Inflamm. 2014, ID983401 (2014)
- Anti-inflammatory effects of BHBA in both in vivo and in vitro Parkinson's disease models are mediated by GPR109A-dependent mechanisms: S.P. Fu, et al.; J. Neuroinflamm. 12, ID9 (2015)
- The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease: Y.H. Youm, et al.; Nat. Med. 21, 263 (2015)
- Taming the inflammasome: M. Levy, et al.; Nat. Med. 21, 213 (2015)
