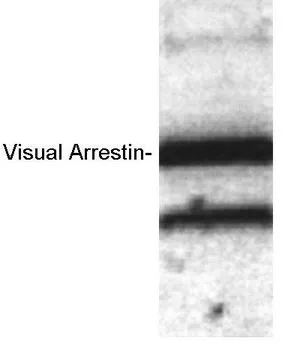
WB analysis of recombinant bovine visual arrestin using GTX23435 S-arrestin antibody.
S-arrestin antibody
GTX23435
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse, Sheep
TargetSAG
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameS-arrestin antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Antibody SpecificityThis antibody detects an ~57 kDa protein representing recombinant bovine and sheep visual arrestin. This antibody also detects a lower molecular weight protein which could correspond to degradation product.
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 2 microg/ml. ICC/IF: 1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID280922
- Target nameSAG
- Target descriptionS-antigen visual arrestin
- Target synonyms48 kDa protein; arrestin1; retinal S-antigen; rod photoreceptor arrestin; S-AG; S-antigen; retina and pineal gland (arrestin); S-arrestin
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP08168
- Protein NameS-arrestin
- Scientific DescriptionVision involves the conversion of light into electrochemical signals that are processed by the retina and subsequently sent to and interpreted by the brain. The process of converting light to an electrochemical signal begins when the membrane-bound protein, rhodopsin, absorbs light within the retina. Photoexcitation of rhodopsin causes the cytoplasmic surface of the protein to become catalytically active. In the active state, rhodopsin activates transducin, a GTP binding protein. Once activated, transducin promotes the hydrolysis of cGMP by phosphodiesterase (PDE). The decrease of intracellular cGMP concentrations causes the ion channels within the outer segment of the rod or cone to close, thus causing membrane hyperpolarization and, eventually, signal transmission. Rhodopsins activity is believed to be shut off by its phosphorylation followed by binding of the soluble protein arrestin. ? Arrestins are cytosolic proteins that are involved in G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) desensitization. Arrestin binding to activated GPCRs is phosphorylation dependent and, once bound, uncouple the GPCR from the associated heterotrimeric G proteins. There are currently 4 known mammalian isoforms, beta-arrestin1 (arrestin2), beta-arrestin2 (arrestin3), visual arrestin (arrestin1), and cone arrestin. The beta- isoforms are ubiquitously expressed and are known to interact with acetylcholine and adrenergic receptors. Visual and cone arrestins are found to interact directly with transducin.
- ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse, Sheep
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
