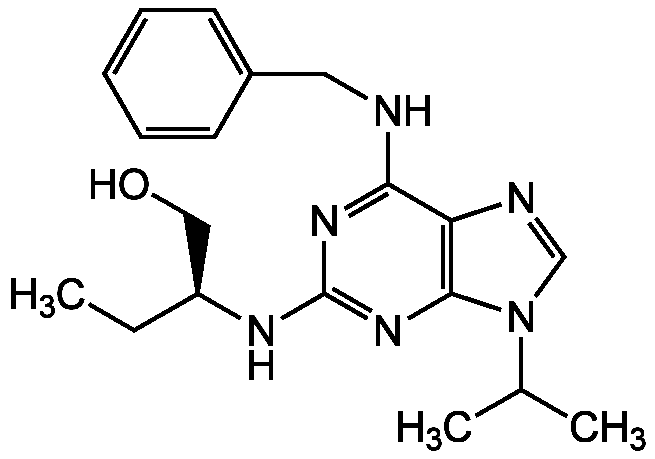
Chemical Structure
(S)-Roscovitine [186692-45-5]

AG-MR-C0002
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Name(S)-Roscovitine [186692-45-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number186692-45-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>99%
- Molecular FormulaC19H26N6O
- Molecular Weight354.5
- Scientific Description(S)-enantiomer of (R)-roscovitine (Prod. No. MR-C0001). Potent selective cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) inhibitor. Potential neuroprotectant for stroke. Crosses the blood brain barrier. Inhibits CDK5, consequently blocking hypoxia-induced apoptosis in neurons. Potential anti-inflammatory compound. Potential antidiabetic compound. - Chemical. CAS: 186692-45-5. Formula: C19H26N6O. MW: 354.5. (S)-enantiomer of (R)-roscovitine (Prod. No. MR-C0001). Potent selective cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) inhibitor. Potential neuroprotectant for stroke. Crosses the blood brain barrier. Inhibits CDK5, consequently blocking hypoxia-induced apoptosis in neurons. Potential anti-inflammatory compound. Potential antidiabetic compound.
- SMILESCC[C@@H](CO)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2C(C)C)C(NCC2=CC=CC=C2)=N1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC51202000
References
- Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5: L. Meijer, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 243, 527 (1997)
- Maintenance of meiotic arrest in bovine oocytes using the S-enantiomer of roscovitine: effects on maturation, fertilization and subsequent embryo development in vitro: P. Coy, et al.; Reprod. 129, 19 (2005)
- Delayed treatment with systemic (S)-roscovitine provides neuroprotection and inhibits in vivo CDK5 activity increase in animal stroke models: B. Menn, et al.; PLoS One 5, e12117 (2010)
