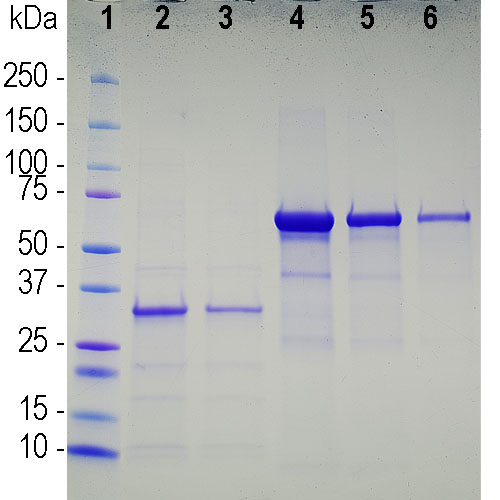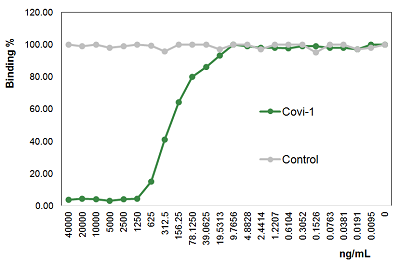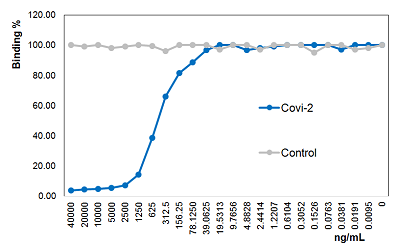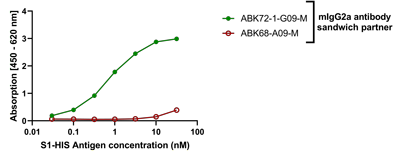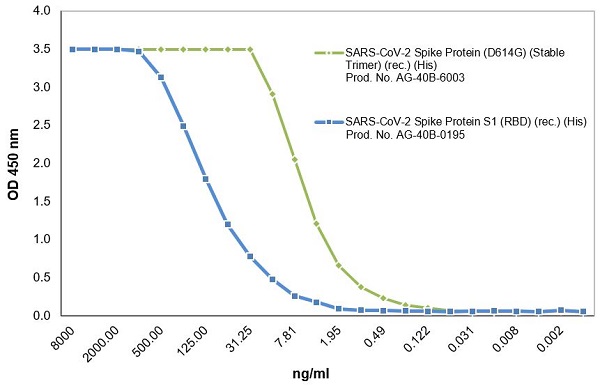
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (D614G) (Stable Trimer) (rec.) (His)
AG-40B-6003
Protein IDP0DTC2
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameSARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (D614G) (Stable Trimer) (rec.) (His)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration0.2 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>90%
- Gene ID43740568
- Target nameS
- Target descriptionsurface glycoprotein
- Target synonymsGU280_gp02, spike glycoprotein, surface glycoprotein
- Protein IDP0DTC2
- Protein NameSpike glycoprotein
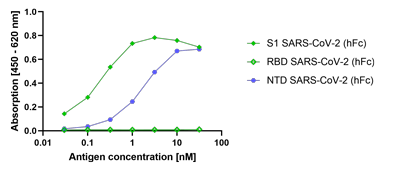
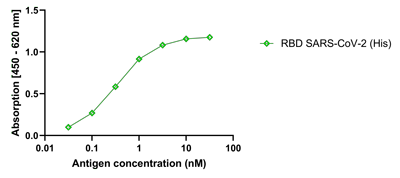
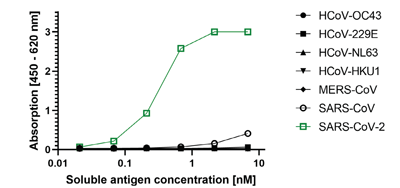
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant protein. Full-length soluble SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein (aa 16-1213) including a foldon trimerization motif, mutated Furin recognition site (R682S, R685S) and two stabilizing mutations (K986P and V987P) is fused at the C-terminus to a His-tag. Binds to the human SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2. Binds to anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike antibodies in serum or plasma. Source: HEK 293 cells. Lyophilized. Contains PBS and 20% glycerol. Purity: >90% (SDS-PAGE). SARS-CoV-2 shares 79.5% sequence identity with SARS-CoV and is 96.2% identical at the genome level to the bat coronavirus BatCoV RaTG133, suggesting it had originated in bats. The original Wuhan strain of the virus has become quickly replaced by its more transmissible variant, mainly determined by a single amino acid point mutation D614G. The coronaviral genome encodes four major structural proteins: the Spike (S) protein, Nucleocapsid (N) protein, Membrane/Matrix (M) protein and the Envelope (E) protein. The SARS Envelope (E) protein contains a short palindromic transmembrane helical hairpin that seems to deform lipid bilayers, which may explain its role in viral budding and virion envelope morphogenesis. The SARS Membrane/Matrix (M) protein is one of the major structural viral proteins. It is an integral membrane protein involved in the budding of the viral particles and interacts with SARS Spike (S) protein and the Nucleocapsid (N) protein. The N protein contains two domains, both of them bind the virus RNA genome via different mechanisms. The CoV Spike (S) protein assembles as trimer and plays the most important role in viral attachment, fusion and entry. It is composed of a short intracellular tail, a transmembrane anchor and a large ectodomain that consists of a receptor binding S1 subunit (RBD domain) and a membrane-fusing S2 subunit. The S1 subunit contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which binds to the cell surface receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) present at the surface of epithelial cells. It has been demonstrated that certain mutations and the inclusion of trimerization motif can stabilize recombinant Spike protein trimers. The recombinant protein SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (D614G) (Stable Trimer) (rec.) (His) could be useful for structural biology research, vaccine development, serological diagnostic kit development or neutralizing antibody screening. - SARS-CoV-2 shares 79.5% sequence identity with SARS-CoV and is 96.2% identical at the genome level to the bat coronavirus BatCoV RaTG133, suggesting it had originated in bats. The original Wuhan strain of the virus has become quickly replaced by its more transmissible variant, mainly determined by a single amino acid point mutation D614G. The coronaviral genome encodes four major structural proteins: the Spike (S) protein, Nucleocapsid (N) protein, Membrane/Matrix (M) protein and the Envelope (E) protein. The SARS Envelope (E) protein contains a short palindromic transmembrane helical hairpin that seems to deform lipid bilayers, which may explain its role in viral budding and virion envelope morphogenesis. The SARS Membrane/Matrix (M) protein is one of the major structural viral proteins. It is an integral membrane protein involved in the budding of the viral particles and interacts with SARS Spike (S) protein and the Nucleocapsid (N) protein. The N protein contains two domains, both of them bind the virus RNA genome via different mechanisms. The CoV Spike (S) protein assembles as trimer and plays the most important role in viral attachment, fusion and entry. It is composed of a short intracellular tail, a transmembrane anchor and a large ectodomain that consists of a receptor binding S1 subunit (RBD domain) and a membrane-fusing S2 subunit. The S1 subunit contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which binds to the cell surface receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) present at the surface of epithelial cells. It has been demonstrated that certain mutations and the inclusion of trimerization motif can stabilize recombinant Spike protein trimers. The recombinant protein SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (D614G) (Stable Trimer) (rec.) (His) could be useful for structural biology research, vaccine development, serological diagnostic kit development or neutralizing antibody screening.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesVirus