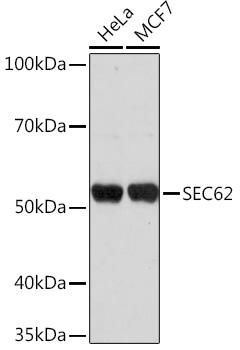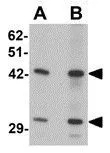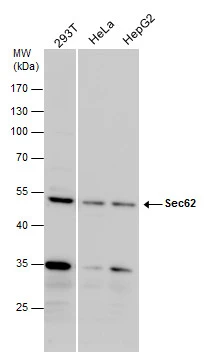
Sec62 antibody detects Sec62 protein by western blot analysis. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Sec62 antibody (GTX129853) diluted by 1:1000.
Sec62 antibody
GTX129853
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSEC62
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSec62 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.07 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7095
- Target nameSEC62
- Target descriptionSEC62 preprotein translocation factor
- Target synonymsDtrp1, HTP1, TLOC1, TP-1, translocation protein SEC62, SEC62 homolog, preprotein translocation factor, hTP-1, membrane protein SEC62, S.cerevisiae, homolog of, translocation protein 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ99442
- Protein NameTranslocation protein SEC62
- Scientific DescriptionThe Sec61 complex is the central component of the protein translocation apparatus of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. The protein encoded by this gene and SEC63 protein are found to be associated with ribosome-free SEC61 complex. It is speculated that Sec61-Sec62-Sec63 may perform post-translational protein translocation into the ER. The Sec61-Sec62-Sec63 complex might also perform the backward transport of ER proteins that are subject to the ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent degradation pathway. The encoded protein is an integral membrane protein located in the rough ER. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Takasugi M, Ohtani N, Takemura K, et al. CD44 correlates with longevity and enhances basal ATF6 activity and ER stress resistance. Cell Rep. 2023,42(9):113130. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113130Read this paper
- An H, Ordureau A, Paulo JA, et al. TEX264 Is an Endoplasmic Reticulum-Resident ATG8-Interacting Protein Critical for ER Remodeling during Nutrient Stress. Mol Cell. 2019,74(5):891-908.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.03.034Read this paper