![IHC-P analysis of human colon carcinoma tissue using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:200 IHC-P analysis of human colon carcinoma tissue using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:200](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX22873/GTX22873_1192_IHC-P_w_23060620_154.webp)
IHC-P analysis of human colon carcinoma tissue using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:200
Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]
GTX22873
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityCanine, Drosophila, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Sheep
TargetATP1B1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:10,000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDM17-P5-F11
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID481
- Target nameATP1B1
- Target descriptionATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit beta 1
- Target synonymsATP1B, sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit beta-1, ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, beta 1 polypeptide, Beta 1-subunit of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase, Na, K-ATPase beta-1 polypeptide, adenosinetriphosphatase, sodium pump subunit beta-1, sodium-potassium ATPase subunit beta 1 (non-catalytic), sodium/potassium-dependent ATPase beta-1 subunit, sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase beta-1 chain
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDP05026
- Protein NameSodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit beta-1
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of Na+/K+ and H+/K+ ATPases beta chain proteins, and to the subfamily of Na+/K+ -ATPases. Na+/K+ -ATPase is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane. These gradients are essential for osmoregulation, for sodium-coupled transport of a variety of organic and inorganic molecules, and for electrical excitability of nerve and muscle. This enzyme is composed of two subunits, a large catalytic subunit (alpha) and a smaller glycoprotein subunit (beta). The beta subunit regulates, through assembly of alpha/beta heterodimers, the number of sodium pumps transported to the plasma membrane. The glycoprotein subunit of Na+/K+ -ATPase is encoded by multiple genes. This gene encodes a beta 1 subunit. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described, but their biological validity is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]
- ReactivityCanine, Drosophila, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Sheep
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Gentil C, Le Guiner C, Falcone S, et al. Dystrophin Threshold Level Necessary for Normalization of Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase, Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase, and Ryanodine Receptor-Calcium Release Channel Type 1 Nitrosylation in Golden Retriever Muscular Dystrophy Dystrophinopathy. Hum Gene Ther. 2016,27(9):712-26. doi: 10.1089/hum.2016.041Read this paper
- Persson AK, Kim I, Zhao P, et al. Sodium channels contribute to degeneration of dorsal root ganglion neurites induced by mitochondrial dysfunction in an in vitro model of axonal injury. J Neurosci. 2013,33(49):19250-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2148-13.2013Read this paper

![IHC-P analysis of human tonsil tissue using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:200 IHC-P analysis of human tonsil tissue using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:200](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX22873/GTX22873_1194_IHC-P_w_23060620_747.webp)
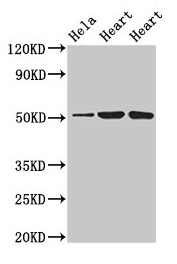
![WB analysis of 25 ug of human brain (lane 1), human liver (lane 2), human kidney (lane 3) and mouse kidney (lane 4) lysates using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Dilution : 1:5000 WB analysis of 25 ug of human brain (lane 1), human liver (lane 2), human kidney (lane 3) and mouse kidney (lane 4) lysates using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Dilution : 1:5000](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX22873/GTX22873_1620_WB_w_23060620_889.webp)
![ICC/IF analysis of MCF-7 cells using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Cells were probed without (right) or with(left) an antibody. Green : Primary antibody Blue : Nuclei Red : Actin Fixation : formaldehyde Dilution : 1:200 overnight at 4oC ICC/IF analysis of MCF-7 cells using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Cells were probed without (right) or with(left) an antibody. Green : Primary antibody Blue : Nuclei Red : Actin Fixation : formaldehyde Dilution : 1:200 overnight at 4oC](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX22873/GTX22873_533_ICC-IF_w_23060620_437.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human liver tissue using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:200 IHC-P analysis of human liver tissue using GTX22873 Sodium/Potassium ATPase beta 1 antibody [M17-P5-F11]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:200](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX22873/GTX22873_1193_IHC-P_w_23060620_647.webp)