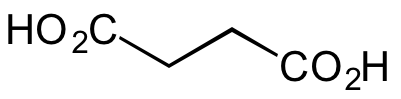
Chemical Structure
Succinic acid [Succinate] [110-15-6]
AG-CN2-0521
CAS Number110-15-6
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>99%
Molecular Weight118.1
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameSuccinic acid [Succinate] [110-15-6]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number110-15-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>99%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC4H6O4
- Molecular Weight118.1
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 110-15-6. Formula: C4H6O4. MW: 118.1. Metabokine that accumulates specifically in brown adipose tissue (BAT) and induces thermogenesis by activating brown fat (BAT). Inflammasome activator through a ROS-dependent pathway. Important in antimicrobial defense. Oncometabolite promoting angiogenesis. Agent to study cancer immunity, involved in both inflammatory diseases and cancer. Important in microbe-microbe interactions in gut microbiota. Useful for immunometabolism research. Intermediate of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle playing a crucial role in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generation in mitochondria. All metabolic pathways that are interlinked with the TCA cycle, including the metabolism of carbohydrates, amino acids, fatty acids, cholesterol and heme, rely on the temporary formation of succinate. Binds to the receptor SUCNR1 (GPR91) triggering intracellular calcium release and inhibits cAMP production, inducing cellular stress. Involved in the formation and elimination of reactive oxygen species, epigenetics, tumorigenesis and inflammation (inflammatory cytokine production). Involved in protein succinylation, a novel posttranslational modification pathway. Mutations in enzymes such as succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) that participate in succinate-related pathways lead to various pathologies, including tumor formation and innate inflammatory processes. High concentration of succinate in tumor microenvironments acts as an active participant in tumorigenesis. Extracellular succinate can act as a signaling molecule with hormone-like function, targeting a variety of tissues such as blood cells, adipose tissue, immune cells, the liver, the heart, the retina and kidney. Re-entry point for the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) shunt into the TCA cycle, a closed cycle which synthesizes and recycles GABA. Used in a wide range of applications in agricultural, food (neutralizing agent), pharmaceutical industries and as building block for dyes or flavouring agents. In addition it can also be used in the synthesis of biodegradable polymers and as a matrix in infrared (IR) MALDI analytical methods. - Metabokine that accumulates specifically in brown adipose tissue (BAT) and induces thermogenesis by activating brown fat (BAT). Inflammasome activator through a ROS-dependent pathway. Important in antimicrobial defense. Oncometabolite promoting angiogenesis. Agent to study cancer immunity, involved in both inflammatory diseases and cancer. Important in microbe-microbe interactions in gut microbiota. Useful for immunometabolism research. Intermediate of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle playing a crucial role in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generation in mitochondria. All metabolic pathways that are interlinked with the TCA cycle, including the metabolism of carbohydrates, amino acids, fatty acids, cholesterol and heme, rely on the temporary formation of succinate. Binds to the receptor SUCNR1 (GPR91) triggering intracellular calcium release and inhibits cAMP production, inducing cellular stress. Succinate is released by muscles during exercice by a pH-gated secretion mechanism via MCT1 (monocarboxylate transporter 1). Released succinate binds to its receptor SUCNR1 (Succinate Receptor 1) to mediate muscle adaptation to exercice training. Involved in the formation and elimination of reactive oxygen species, epigenetics, tumorigenesis and inflammation (inflammatory cytokine production). Involved in protein succinylation, a novel posttranslational modification pathway. Mutations in enzymes such as succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) that participate in succinate-related pathways lead to various pathologies, including tumor formation and innate inflammatory processes. High concentration of succinate in tumor microenvironments acts as an active participant in tumorigenesis. Extracellular succinate can act as a signaling molecule with hormone-like function, targeting a variety of tissues such as blood cells, adipose tissue, immune cells, the liver, the heart, the retina and kidney. Re-entry point for the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) shunt into the TCA cycle, a closed cycle which synthesizes and recycles GABA. Used in a wide range of applications in agricultural, food (neutralizing agent), pharmaceutical industries and as building block for dyes or flavouring agents. In addition it can also be used in the synthesis of biodegradable polymers and as a matrix in infrared (IR) MALDI analytical methods.
- SMILESO=C(CCC(O)=O)O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC12352200


![Succinic acid [110-15-6] [110-15-6]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/2F/CgoaEGY7K2mEC13QAAAAAK7LwHM670.png)