Chemical Structure
TOFA [54857-86-2]

AG-CR1-2905
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameTOFA [54857-86-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number54857-86-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC19H32O4
- Molecular Weight324.5
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 54857-86-2. Formula: C19H32O4. MW: 324.5. . Fatty acid synthase (FASN) inhibitor. Cell-permeable, potent, reversible and competitive inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) consequently bocking the synthesis of malonyl-CoA. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Anticancer agent. Induces apoptosis in a variety of tumor cell lines. Relatively non-cytotoxic to various cancer cell lines. TOFA-induced reduction in malonyl-CoA is reported to off-set the effect of C75 on food intake in fasted mice and on apoptosis in tumor cells. Hypolipidemic agent. Stimulates citrate accumulation in the cell, which leads to a suppression of glycolysis by citrate-induced inhibition of phosphofructokinase. - Fatty acid synthase (FASN) inhibitor. Cell permeable, potent, reversible and competitive inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) consequently blocking the synthesis of malonyl-CoA. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Anticancer agent. Induces apoptosis in a variety of tumor cell lines. Relatively non-cytotoxic to various cancer cell lines. TOFA-induced reduction in malonyl-CoA is reported to off-set the effect of C75 (AG-CR1-2904) on food intake in fasted mice and on apoptosis in tumor cells. Hypolipidemic agent. Stimulates citrate accumulation in the cell, which leads to a suppression of glycolysis by citrate-induced inhibition of phosphofructokinase.
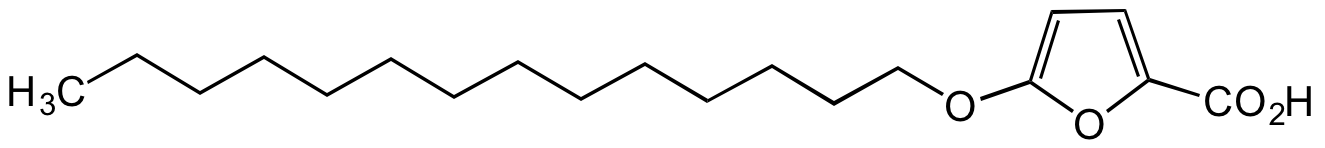
- SMILESCCCCCCCCCCCCCCOC1=CC=C(C(O)=O)O1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- 5-(Tetradecyloxy)-2-furancarboxylic acid and related hypolipidemic fatty acid-like alkyloxyarylcarboxylic acids: R.A. Parker, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 20, 781 (1977)
- Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis in isolated adipocytes by 5-(tetradecyloxy)-2-furoic acid: D.L. Halvorson & S.A. McCune; Lipids 19, 851 (1984)
- Pharmacological inhibitors of mammalian fatty acid synthase suppress DNA replication and induce apoptosis in tumor cell lines: E.S. Pizer, et al.; Cancer Res. 58, 4611 (1998)
- Reduced food intake and body weight in mice treated with fatty acid synthase inhibitors: T.M. Loftus, et al.; Science 288, 2379 (2000)
- Fatty acid synthase inhibition in human breast cancer cells leads to malonyl-CoA-induced inhibition of fatty acid oxidation and cytotoxicity: J.N. Thupari, et al.; BBRC 285, 217 (2001)
- Fatty acid synthase inhibition triggers apoptosis during S phase in human cancer cells: W. Zhou, et al.; Cancer Res. 63, 7330 (2003)
- C75, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor, modulates AMP-activated protein kinase to alter neuronal energy metabolism: L.E. Landree, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 279, 3817 (2004)
- TOFA (5-tetradecyl-oxy-2-furoic acid) reduces fatty acid synthesis, inhibits expression of AR, neuropilin-1 and Mcl-1 and kills prostate cancer cells independent of p53 status: N.V. Guseva, et al.; Cancer Biol. Ther. 12, 80 (2011)
- A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists: L.A. O'Neill, et al.; Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 553 (2016)
