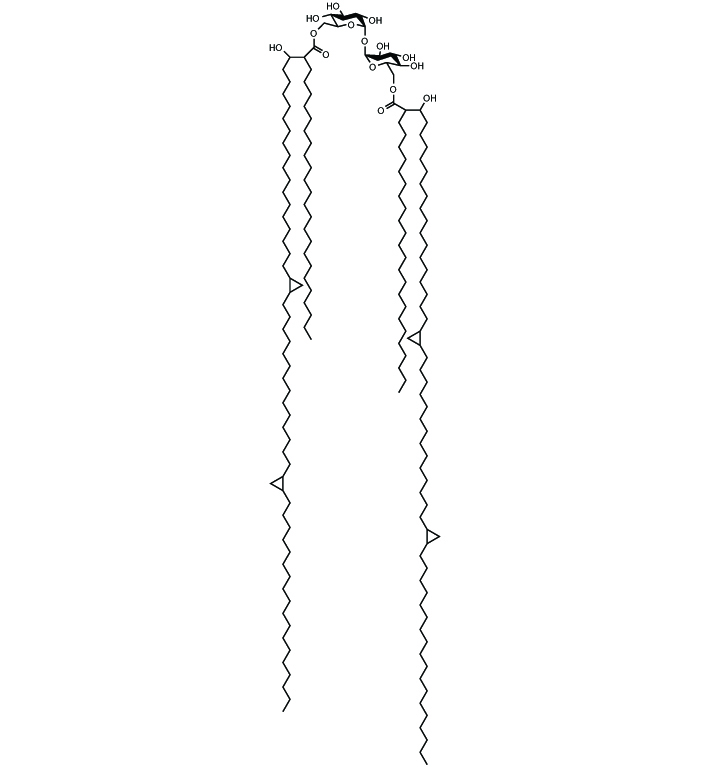
Chemical Structure
Trehalose 6,6-dimycolate (TDM) [Cord Factor] Endotoxin-free (sterile) [61512-20-7] [61512-20-7]
IAX-200-101
Product group Molecular Biology
Overview
- SupplierInnaxon
- Product NameTrehalose 6,6-dimycolate (TDM) [Cord Factor] Endotoxin-free (sterile) [61512-20-7] [61512-20-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number61512-20-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 61512-20-7. Isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The mycobacterial glycolipid trehalose-6,6-dimycolate (TDM), also named Cord Factor (CF), is an important regulator of immune responses during Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infections. Macrophages recognize TDM through the Mincle receptor and initiate TDM-induced inflammatory responses, leading to lung granuloma formation. Controlled use of its cell wall activates macrophages in ways that can be harnessed for therapy. For example, M. bovis Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) is one of the most widely used antitumor adjuvant therapies in humans. Freunds adjuvant, an emulsion of mycobacterial cell wall components in paraffin oil, is mixed with antigens to optimize memory T and B cell responses in mice. TDM along with a detoxified derivative of Lipid A (MPLA) and cell wall skeleton make up a formulation also known under the name of Ribi adjuvant. Recent studies suggest that Mincle is a pivotal receptor for the mycobacterial cord factor. However, additional receptors may bind TDM independently or in cooperation with Mincle. Candidates include other CLEC proteins, such as Dectin-2, which also associates with FcRg, is expressed in macrophages, and binds to Mtb. The scavenger receptor MARCO interacts with TDM, yet lacks an intracellular domain for signal initiation. In contrast, Mincle can directly trigger Syk-Card9 signaling via its association with FcRg. Whereas in the absence of Mincle macrophages did not respond to TDM, a recent report found Mincle-deficient mice capable of mounting an efficient granulomatous and protective immune response after low and high doseinfections with Mtb. Mutant mice generated a normal T helper (TH)1 and TH17 immune response followed by the induction of efficient macrophage effector mechanisms and control of mycobacterial growth identical to wildtype mice. The absence of the innate receptor Mincle may be fully compensated for in vivo in terms of sensing Mtb and mounting a protective inflammatory immune response. - The mycobacterial glycolipid trehalose-6,6-dimycolate (TDM), also named Cord Factor (CF), is an important regulator of immune responses during Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infections. Macrophages recognize TDM through the Mincle receptor and initiate TDM-induced inflammatory responses, leading to lung granuloma formation. Controlled use of its cell wall activates macrophages in ways that can be harnessed for therapy. For example, M. bovis Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) is one of the most widely used antitumor adjuvant therapies in humans. Freunds adjuvant, an emulsion of mycobacterial cell wall components in paraffin oil, is mixed with antigens to optimize memory T and B cell responses in mice. TDM along with a detoxified derivative of Lipid A (MPLA) and cell wall skeleton make up a formulation also known under the name of Ribi adjuvant. Recent studies suggest that Mincle is a pivotal receptor for the mycobacterial cord factor. However, additional receptors may bind TDM independently or in cooperation with Mincle. Candidates include other CLEC proteins, such as Dectin-2, which also associates with FcRg, is expressed in macrophages, and binds to Mtb. The scavenger receptor MARCO interacts with TDM, yet lacks an intracellular domain for signal initiation. In contrast, Mincle can directly trigger Syk-Card9 signaling via its association with FcRg. Whereas in the absence of Mincle macrophages did not respond to TDM, a recent report found Mincle-deficient mice capable of mounting an efficient granulomatous and protective immune response after low and high doseinfections with Mtb. Mutant mice generated a normal T helper (TH)1 and TH17 immune response followed by the induction of efficient macrophage effector mechanisms and control of mycobacterial growth identical to wildtype mice. The absence of the innate receptor Mincle may be fully compensated for in vivo in terms of sensing Mtb and mounting a protective inflammatory immune response.
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41115813
