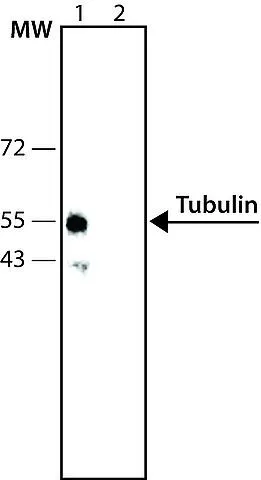
WB analysis of mouse brain extract using GTX11270 Tubulin antibody. Lane 1 : Antibody dilution 1:500 Lane 2 : Negative control (without primary antibody)
Tubulin antibody
GTX11270
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityChicken, Mouse
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameTubulin antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Antibody SpecificityThe product stains tubulin in cultured chicken fibroblasts or 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Additional bands may be stained in immunoblotting.
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:200. ICC/IF: 1:80. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionThe major building block of microtubules is tubulin, an intracellular cylindrical filamentous structure that is present in almost all eukaryotic cells. Except in the simplest eukaryotes, tubulin (100 kDa) exists in all cells as a heterodimer of two similar but non-identical polypeptides (55 kDa each), designated alpha and beta, that assemble into microtubules. Within either family of alpha/beta tubulin heterodimers, individual subunits diverge from each other (both within and across species) at less than 10% of the amino acid positions. The most extreme diversity is localized to the carboxyl-terminal 15 residues. Both alpha and beta tubulins consist of various isotypes. In addition, both undergo post-translational modifications, including acetylation, phosphorylation detyrosination, polyglutamylation, and polyglycylation. Polyglutamylation of tubulin consists of the addition of a lateral chain of glutamyl units on the C-terminal region of tubulin polypeptides. This modification was shown to regulate the interaction between tau, one of the major neuronal microtubule associated proteins, and tubulin. Furthermore, it was shown that injection of monoclonal antibodies specific to the polyglutamylated form of tubulin into HeLa cells caused the disappearance of centrioles, an organelle known to have the most stable microtubules. The detection, localization, and characterization of proteins involved in microtubule function is fundamental to the understanding of mitosis, meiosis, organellar and flagellar movement, intracellular transport, and cytoskeletal functions. Antibodies reacting specifically with the modified forms of alpha and beta tubulin isotypes serve as essential tools in the detection and study of the functional significance of these molecules.
- ReactivityChicken, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203