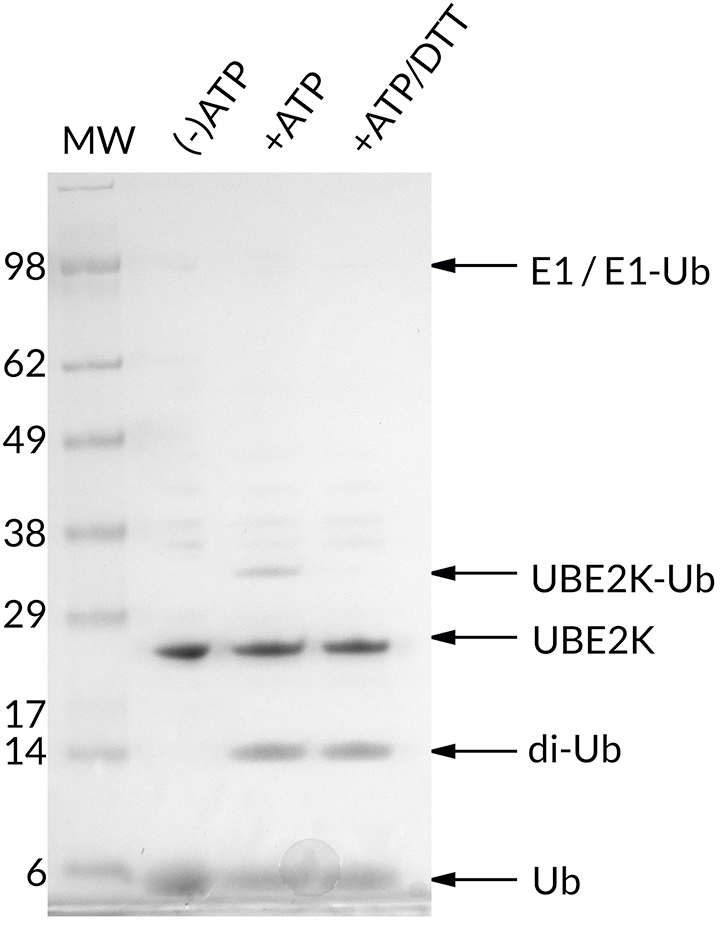
Thioester Activity Assay: UBE2K forms a thioester with Ub in an ATP-dependent manner and the bond can be reduced with addition of excess DTT. The thioester assay also shows di-ubiquitin formation with addition of ATP. This confirms the activity of
UbcH1/UBE2K/E2-25K (human) (rec.) (His)
SBB-CE0022
Protein IDP61086
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierSouth Bay Bio
- Product NameUbcH1/UBE2K/E2-25K (human) (rec.) (His)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID3093
- Target nameUBE2K
- Target descriptionubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 K
- Target synonymsE2-25K, HIP2, HYPG, LIG, UBC1, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 K, E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme K, E2(25K), HIP-2, huntingtin-interacting protein 2, ubiquitin carrier protein, ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2K, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2(25K), ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2-25 KDA, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2K (UBC1 homolog, yeast), ubiquitin-protein ligase
- Protein IDP61086
- Protein NameUbiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 K
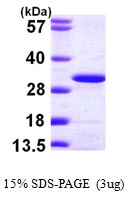
- Scientific DescriptionProtein. Human UBE2K (aa 1-200)is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag. Source: E. coli. Formulation: Liquid. In 50mM HEPES pH 7.5, 150mM sodium chloride, 10% glycerol (v/v), 2mM TCEP. Purity: >95% (SDS-PAGE). UBE2K (UbcH1) is an E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme. An E1 activating enzyme is required to attach ubiquitin to UBE2K via an active site cysteine. The mechanism of ubiquitin transfer involves the breaking of a E1-Ub thioester linkage, followed by a reformation of a UBE2K-Ub thioester. UBE2K is capable of synthesizing K48-linked ubiquitin chains and can do so without an E3 ubiquitin ligating enzyme present.UbcH1 catalyzes free K48-linked polyubiquitin chains and is known to interact with huntingtin and TRIM6. Although an E3 ligase is not required for chain formation, free UBE2K synthesized K48 polyubiquitin chains have been shown to interact with the E3 TRIM6, leading to activation of IKKepsilon kinase activity and subsequent antiviral activity. - UBE2K (UbcH1) is an E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme. An E1 activating enzyme is required to attach ubiquitin to UBE2K via an active site cysteine. The mechanism of ubiquitin transfer involves the breaking of a E1-Ub thioester linkage, followed by a reformation of a UBE2K-Ub thioester. UBE2K is capable of synthesizing K48-linked ubiquitin chains and can do so without an E3 ubiquitin ligating enzyme present. UBE2K catalyzes free K48-linked polyubiquitin chains and is known to interact with huntingtin and TRIM6. Although an E3 ligase is not required for chain formation, free UBE2K synthesized K48 polyubiquitin chains have been shown to interact with the E3 TRIM6, leading to activation of IKKepsilon kinase activity and subsequent antiviral activity.
- Storage Instruction-80°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman