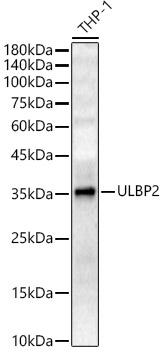
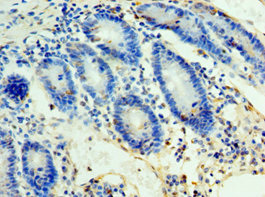
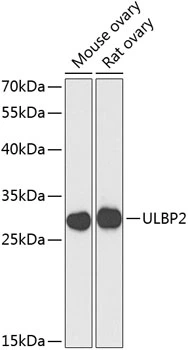
ULBP2 antibody [7F33]
GTX53048
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Neutralisation/Blocking
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetULBP2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameULBP2 antibody [7F33]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteFCM: 1:50 - 1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Neutralisation/Blocking
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID7F33
- Concentration500 ug/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID80328
- Target nameULBP2
- Target descriptionUL16 binding protein 2
- Target synonymsALCAN-alpha, N2DL2, NKG2DL2, RAET1H, RAET1L, UL16-binding protein 2, NKG2D ligand 2, retinoic acid early transcript 1H, retinoic acid early transcript 1L
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2
- Protein IDQ9BZM5
- Protein NameUL16-binding protein 2
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-related molecule that binds to the NKG2D receptor on natural killer (NK) cells to trigger release of multiple cytokines and chemokines that in turn contribute to the recruitment and activation of NK cells. The encoded protein undergoes further processing to generate the mature protein that is either anchored to membrane via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol moiety, or secreted. Many malignant cells secrete the encoded protein to evade immunosurveillance by NK cells. This gene is located in a cluster of multiple MHC class I-related genes on chromosome 6. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- FBXO44 promotes DNA replication-coupled repetitive element silencing in cancer cells. Shen JZ et al., 2021 Jan 21, CellRead this paper