![VAMP2 antibody [GT6311] detects VAMP2 protein by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV9 rat E18 primary hippocampal neuron cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: VAMP2 stained by VAMP2 antibody [GT6311] (GTX634812) diluted at 1:500. Red: NeuN, stained by NeuN antibody (GTX132974) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). VAMP2 antibody [GT6311] detects VAMP2 protein by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV9 rat E18 primary hippocampal neuron cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: VAMP2 stained by VAMP2 antibody [GT6311] (GTX634812) diluted at 1:500. Red: NeuN, stained by NeuN antibody (GTX132974) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634812/GTX634812_43409_20190306_ICC_IF_R_w_23061202_709.webp)
VAMP2 antibody [GT6311] detects VAMP2 protein by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV9 rat E18 primary hippocampal neuron cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: VAMP2 stained by VAMP2 antibody [GT6311] (GTX634812) diluted at 1:500. Red: NeuN, stained by NeuN antibody (GTX132974) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
VAMP2 antibody [GT6311]
GTX634812
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetVAMP2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameVAMP2 antibody [GT6311]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDGT6311
- Concentration1.74 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6844
- Target nameVAMP2
- Target descriptionvesicle associated membrane protein 2
- Target synonymsNEDHAHM, SYB2, VAMP-2, vesicle-associated membrane protein 2, synaptobrevin 2
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP63027
- Protein NameVesicle-associated membrane protein 2
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a member of the vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)/synaptobrevin family. Synaptobrevins/VAMPs, syntaxins, and the 25-kD synaptosomal-associated protein SNAP25 are the main components of a protein complex involved in the docking and/or fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane. This gene is thought to participate in neurotransmitter release at a step between docking and fusion. The protein forms a stable complex with syntaxin, synaptosomal-associated protein, 25 kD, and synaptotagmin. It also forms a distinct complex with synaptophysin. It is a likely candidate gene for familial infantile myasthenia (FIMG) because of its map location and because it encodes a synaptic vesicle protein of the type that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of FIMG. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

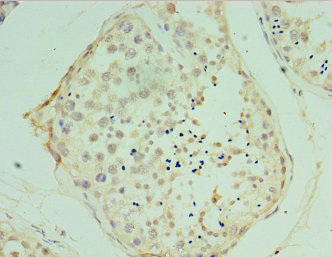
![VAMP2 antibody [GT6311] detects VAMP2 protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse eye. Green: VAMP2 stained by VAMP2 antibody [GT6311] (GTX634812) diluted at 1:500. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 antibody (GTX130245) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min VAMP2 antibody [GT6311] detects VAMP2 protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse eye. Green: VAMP2 stained by VAMP2 antibody [GT6311] (GTX634812) diluted at 1:500. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 antibody (GTX130245) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634812/GTX634812_43409_20190118_IHC-P-FL_M_w_23061202_763.webp)
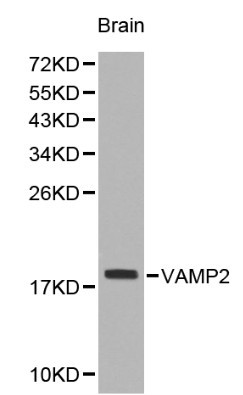
![Various tissue extracts (50 μg) were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with VAMP2 [GT6311] (GTX634812) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Various tissue extracts (50 μg) were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with VAMP2 [GT6311] (GTX634812) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634812/GTX634812_43409_20181207_WB_M_R_w_23061202_929.webp)




![VAMP2 antibody detects VAMP2 protein at synaptic vesicles by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV9 rat E18 primary cortical neurons were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: VAMP2 protein stained by VAMP2 antibody (GTX121462) diluted at 1:500. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 antibody [GT11710] (GTX631836) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX121462/GTX121462_40513_20170503_IFA_R_w_23060519_797.webp)
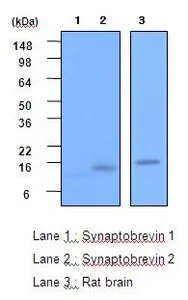
![Various tissue extracts (50 μg) were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with VAMP2 antibody [GT766] (GTX634829) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634829/GTX634829_43766_20191122_WB_M_R_w_23061202_566.webp)