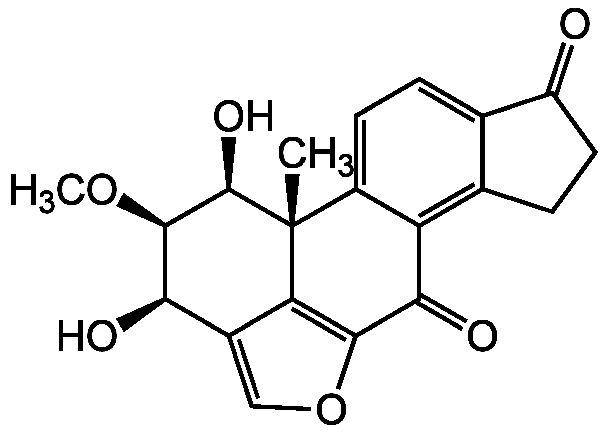
Chemical Structure
Viridiol [23820-80-6]

AG-CN2-0126
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameViridiol [23820-80-6]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number23820-80-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC20H18O6
- Molecular Weight354.4
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 23820-80-6. Formula: C20H18O6. MW: 354.4. Isolated from Trichoderma sp. Steroidal antibiotic. Belongs to the Viridin family, including Wortmannin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0023 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cn2-0023/wortmannin.html ). Antifungal. Phytotoxin. Shows necrotic activity on plants. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor. - Steroidal antibiotic. Belongs to the Viridin family, including Wortmannin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0023 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cn2-0023/wortmannin.html ). Antifungal. Phytotoxin. Shows necrotic activity on plants. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor.
- SMILESCO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)C2=COC3=C2[C@](C)([C@@H]1O)C1=CC=C2C(=O)CCC2=C1C3=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Viridiol, a steroid-like product from Trichoderma viride: J.S. Moffatt, et al.; J. Chem. Soc. D, 1969, 839a (1969)
- Conversion of viridin to viridiol by viridin-producing fungi: R.W. Jones & J.G. Hancock; Can. J. Microbiol. 33, 963 (1987)
- The biosynthesis of the steroid, viridiol, by Gliocladium deliquescens: R. James, et al.; Phytochemistry 27, 387 (1988)
- Plant Growth Response to the Phytotoxin Viridiol Produced by the Fungus Gliocladium virens: R.W. Jones, et al.; Weed Sci. 36, 683 (1988)
- Isolation, identification and necrotic activity of viridiol from Chalara fraxinea, the fungus responsible for dieback of ash: P.F. Andersson, et al.; Forest Pathol. 40, 43 (2010)
- Asterogynins: secondary metabolites from a Costa Rican endophytic fungus: S. Cao, et al.; Org. Lett. 12, 4661 (2010)
