Chemical Structure
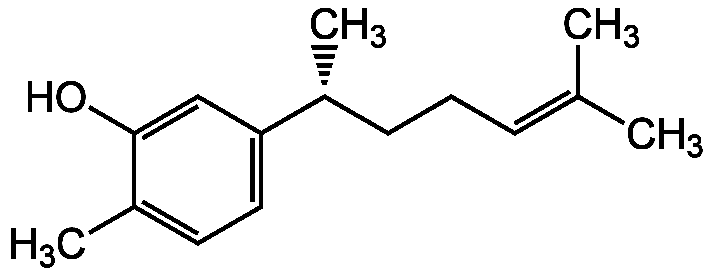
Xanthorrhizol [30199-26-9]

AG-CN2-0090
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameXanthorrhizol [30199-26-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number30199-26-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- FormulationLiquid
- Hazard InformationDanger
- Molecular FormulaC15H22O
- Molecular Weight218.3
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 30199-26-9. Formula: C15H22O. MW: 218.3. Isolated from Curcuma xanthorrhiza. Shows calcium-antagonistic and vasorelaxant activity. Antibacterial. Anti-inflammatory. Potent COX-2 and inducible nitric oxide (iNOS; NOS II) inhibitor. Hepatoprotective. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer. Neuroprotective antioxidant. Antifungal. - Shows calcium-antagonistic and vasorelaxant activity [1,3]. Antibacterial [2]. Anti-inflammatory. Potent COX-2 and inducible nitric oxide (iNOS; NOS II) inhibitor [4,5,9]. Hepatoprotective [5, 6]. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer [7,8,10,12]. Neuroprotective antioxidant [8]. Antifungal [11].
- SMILESC[C@H](CCC=C(C)C)C1=CC=C(C)C(O)=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Effect of xanthorrhizol, xanthorrhizol glycoside and trachylobanoic acid isolated from Cachani complex plants upon the contractile activity of uterine smooth muscle: H. Ponce-Monter, et al.; Phytother. Res. 13, 202 (1999)
- Antibacterial activity of xanthorrhizol from Curcuma xanthorrhiza against oral pathogens: J.K. Hwang, et al.; Fitoterapia 71, 321 (2000)
- Xanthorrhizol induces endothelium-independent relaxation of rat thoracic aorta: M.G. Campos, et al.; Life Sci. 67, 327 (2000)
- Suppressive effect of natural sesquiterpenoids on inducible cyclooxygenase (COX-2) and nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activity in mouse macrophage cells: S.K. Lee, et al.; J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 21, 141 (2002)
- Abrogation of cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity in mice by xanthorrhizol is related to its effect on the regulation of gene transcription: S.H. Kim, et al.; Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 196, 346 (2004)
- Phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal Kinases (JNKs) is involved in the preventive effect of xanthorrhizol on cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity: K.O. Hong, et al.; Arch. Toxicol. 79, 231 (2005)
- Xanthorrhizol induces apoptosis via the up-regulation of bax and p53 in HeLa cells: N. Ismail, et al.; Anticancer Res. 25, 2221 (2005)
- Antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities of xanthorrhizol in hippocampal neurons and primary cultured microglia: C.S. Lim, et al.; J. Neurosci. Res. 82, 831 (2005)
- Regulation of p53-, Bcl-2- and caspase-dependent signaling pathway in xanthorrhizol-induced apoptosis of HepG2 hepatoma cells: T. Handayani, et al.; Anticancer Res. 27, 965 (2007)
- Xanthorrhizol inhibits 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced acute inflammation and two-stage mouse skin carcinogenesis by blocking the expression of ornithine decarboxylase, cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase through mitogen-acti: W.Y. Chung, et al.; Carcinogenesis 28, 1224 (2007)
