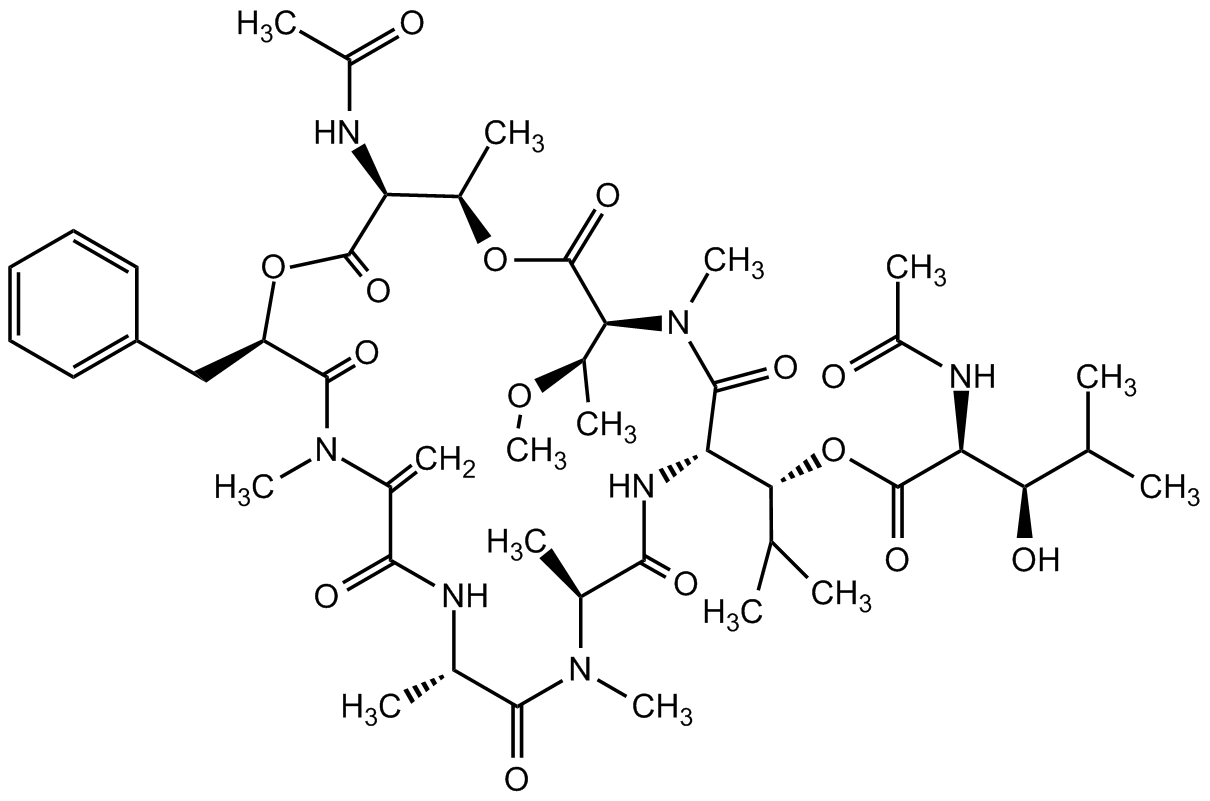
Chemical Structure
YM-254890 [568580-02-9]
AG-CN2-0509
CAS Number568580-02-9
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight960.1
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameYM-254890 [568580-02-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number568580-02-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC46H69N7O15
- Molecular Weight960.1
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 568580-02-9. Formula: C46H69N7O15. MW: 960.1. Cyclic depsipeptide composed of unique amino acids differing from normal amino acids. Membrane permeable, potent and selective Galphaq family inhibitor. Inhibits the signal transduction of Galphaq, Galpha11 and Galpha14 (IC50=0.095microM) by blocking the exchange of GDP for GTP, preventing the activation of the G protein. Inhibits platelet aggregation induced by ADP. Shown to inhibit Galphaq-coupled GPCR signaling by inhibiting calcium mobilization and to have antithrombotic and thrombolytic effects. Might be used as a starting point for new approaches in cancer drug discovery. Galphaq signaling has been shown to regulate brown/beige adipocytes using the structurally similar specific Galphaq family inhibitor FR900359. It is suggested that inhibition of this pathway may be a novel therapeutic approach to combat obesity. The closely related compounds YM-254890 and FR900359 (UBO-QIC) are both potent and selective Galphaq family inhibitors and were for long time only restricted accessible. The commercial availablilty of YM-254890 might give further insights into Galphaq family singaling processes. - Cyclic depsipeptide composed of unique amino acids differing from normal amino acids. Membrane permeable, potent and selective Galphaq family inhibitor. Acts in both in vivo and in vitro systems. Inhibits the signal transduction of Galphaq, Galpha11 and Galpha14 (IC50=0.095microM) by blocking the exchange of GDP for GTP, preventing the activation of the G protein. Inhibits platelet aggregation induced by ADP. Shown to inhibit Galphaq-coupled GPCR signaling by inhibiting calcium mobilization and to have antithrombotic and thrombolytic effects. Might be used as a starting point for new approaches in cancer drug discovery. Galphaq signaling has been shown to regulate brown/beige adipocytes using the structurally similar specific Galphaq family inhibitor FR900359. It is suggested that inhibition of this pathway may be a novel therapeutic approach to combat obesity. The closely related compounds YM-254890 and FR900359 (UBO-QIC) are both potent and selective Galphaq family inhibitors and were for long time only restricted accessible. The commercial availability of YM-254890 might give further insights into Galphaq family signaling processes.
- SMILESO=C(N(C)C(C(N[C@H](C(N(C)[C@H](C(N[C@@H]([C@@H](C(C)C)OC([C@@H](NC(C)=O)[C@@H](C(C)C)O)=O)C1=O)=O)C)=O)C)=O)=C)[C@H](OC([C@@H](NC(C)=O)[C@@H](C)OC([C@@H](N1C)[C@@H](C)OC)=O)=O)CC2=CC=CC=C2
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![YM-254890 [568580-02-9]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/36/13/CgoaEWayN1eEGeZjAAAAAO_zTMk883.png)
