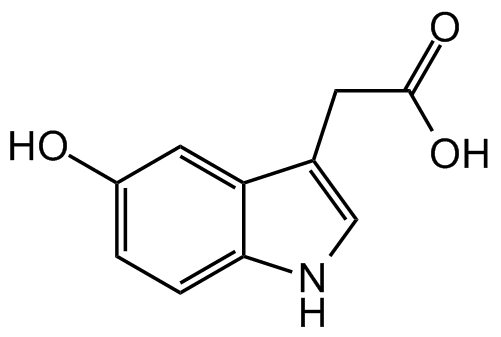
Chemical Structure
5-Hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid [54-16-0] [54-16-0]
AG-CR1-3544
CAS Number54-16-0
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight191.2
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Name5-Hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid [54-16-0] [54-16-0]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number54-16-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC10H9NO3
- Molecular Weight191.2
- Scientific Description5-hydroxy Indole-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA) is the primary metabolite of serotonin, metabolized by monoamine oxidase and aldehyde dehydrogenase in the liver. As the catabolic end product of the serotonin pathway, 5-HIAA is present in body fluids like cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), blood and urine. It can be used as an internal standard for the quantification of serotonin metabolism. 5-HIAA is a potent GPR35 receptor ligand, an inflammatory mediator for immune and non-immune cell populations. 5-HIAA is secreted by platelets and mast cells during inflammation and by binding to neutrophils has a chemoattractant role. 5-HIAA deficient mice show a loss of GPR35-mediated neutrophil recruitment to inflamed tissue. The chemoattractant GPR35-5-HIAA receptor-ligand system cooperates with other inflammation-induced factors in mediating neutrophil recruitment to sites of inflammation. 5-HIAA is excreted in urine and has been used as a biomarker for the detection of neuroendocrine tumors, Celiac disease and Whipple disease, where serotonin expression levels are increased. It also has been associated with metabolic syndrome and low-grade inflammation. 5-HIAA levels are low in CSF in patients with bipolar 1 disorder with childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or sepiapterin reductase deficiency. 5-HIAA has also been associated with autism, insomnia and chronic migraine and is used as a marker for alcohol abuse. - Chemical. CAS: 54-16-0. Formula: C10H9NO3. Molecular Weight: 191.2. 5-hydroxy Indole-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA) is the primary metabolite of serotonin, metabolized by monoamine oxidase and aldehyde dehydrogenase in the liver. As the catabolic end product of the serotonin pathway, 5-HIAA is present in body fluids like cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), blood and urine. It can be used as an internal standard for the quantification of serotonin metabolism. 5-HIAA is a potent GPR35 receptor ligand, an inflammatory mediator for immune and non-immune cell populations. 5-HIAA is secreted by platelets and mast cells during inflammation and by binding to neutrophils has a chemoattractant role. 5-HIAA deficient mice show a loss of GPR35-mediated neutrophil recruitment to inflamed tissue. The chemoattractant GPR35-5-HIAA receptor-ligand system cooperates with other inflammation-induced factors in mediating neutrophil recruitment to sites of inflammation. 5-HIAA is excreted in urine and has been used as a biomarker for the detection of neuroendocrine tumors, Celiac disease and Whipple disease, where serotonin expression levels are increased. It also has been associated with metabolic syndrome and low-grade inflammation. 5-HIAA levels are low in CSF in patients with bipolar 1 disorder with childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or sepiapterin reductase deficiency. 5-HIAA has also been associated with autism, insomnia and chronic migraine and is used as a marker for alcohol abuse.
- SMILESOC1=CC=C(NC=C2CC(O)=O)C2=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![5-HYDROXYINDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID [54-16-0] [54-16-0]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/34/6C/CgoaEWarc7CEXevSAAAAAD94iuw856.png)