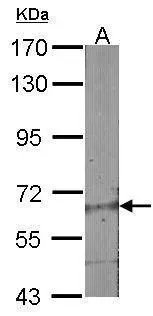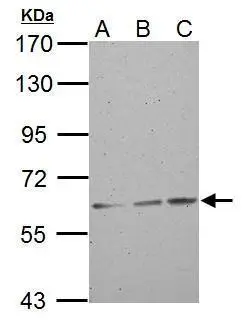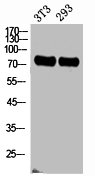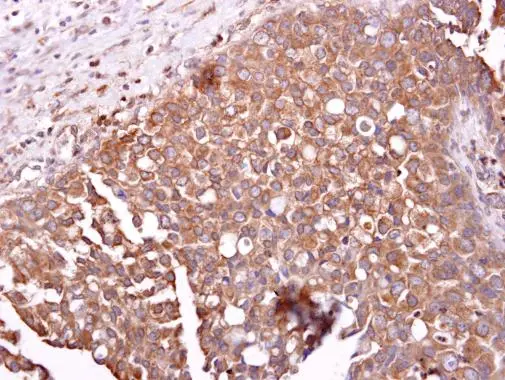
ABCG2 antibody detects ABCG2 protein at cytosol on human breast carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: ABCG2 antibody (GTX100437) dilution: 1:250.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min
ABCG2 antibody
GTX100437
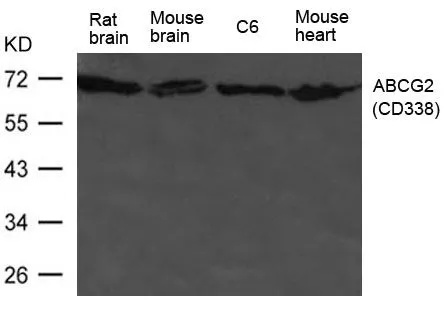
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetABCG2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameABCG2 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID9429
- Target nameABCG2
- Target descriptionATP binding cassette subfamily G member 2 (JR blood group)
- Target synonymsABC15, ABCP, BCRP, BCRP1, BMDP, CD338, CDw338, CDw388, EST157481, GOUT1, MRX, MXR, MXR-1, MXR1, UAQTL1, broad substrate specificity ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2, ABC transporter, ATP binding cassette subfamily G member 2 (Junior blood group), ATP-binding cassette transporter G2, ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 2 (Junior blood group), ATPbinding cassette transporter ABCG2, breast cancer resistance protein, broad substrate specificity ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2 isoform 1 (Junior blood group), mitoxantrone resistance-associated protein, multi drug resistance efflux transport ATP-binding cassette sub-family G (WHITE) member 2, placenta specific MDR protein, placenta-specific ATP-binding cassette transporter, urate exporter
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9UNQ0
- Protein NameBroad substrate specificity ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2
- Scientific DescriptionThe membrane-associated protein encoded by this gene is included in the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the White subfamily. Alternatively referred to as a breast cancer resistance protein, this protein functions as a xenobiotic transporter which may play a major role in multi-drug resistance. It likely serves as a cellular defense mechanism in response to mitoxantrone and anthracycline exposure. Significant expression of this protein has been observed in the placenta, which may suggest a potential role for this molecule in placenta tissue. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161