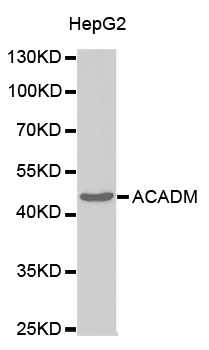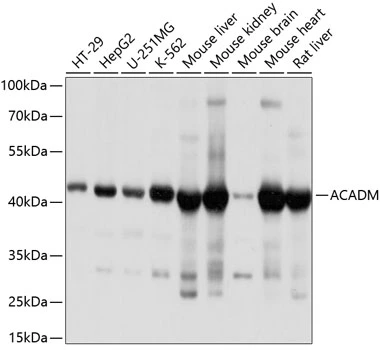
WB analysis of various sample lysates using GTX32421 ACADM antibody. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25microg per lane
ACADM antibody
GTX32421
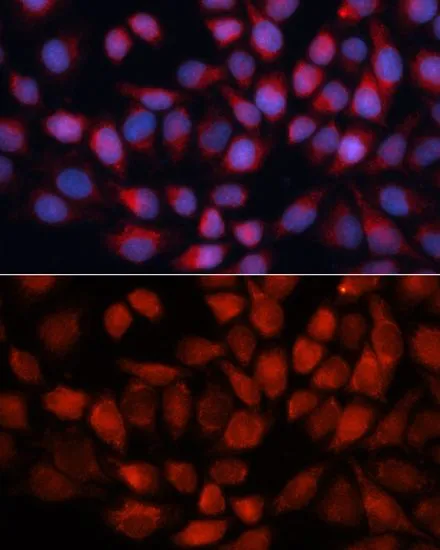
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
TargetACADM
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameACADM antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. ICC/IF: 1:50 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID34
- Target nameACADM
- Target descriptionacyl-CoA dehydrogenase medium chain
- Target synonymsACAD1, MCAD, MCADH, medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, C-4 to C-12 straight chain, acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase, C-4 to C-12 straight chain, medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, testicular tissue protein Li 7
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP11310
- Protein NameMedium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes the medium-chain specific (C4 to C12 straight chain) acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase. The homotetramer enzyme catalyzes the initial step of the mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation pathway. Defects in this gene cause medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, a disease characterized by hepatic dysfunction, fasting hypoglycemia, and encephalopathy, which can result in infantile death. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Gonzalez-Hurtado E, Lee J, Choi J, et al. Fatty acid oxidation is required for active and quiescent brown adipose tissue maintenance and thermogenic programing. Mol Metab. 2018,7:45-56. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.11.004Read this paper
- Gonzalez-Hurtado E, Lee J, Choi J, et al. Loss of macrophage fatty acid oxidation does not potentiate systemic metabolic dysfunction. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2017,312(5):E381-E393. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00408.2016Read this paper