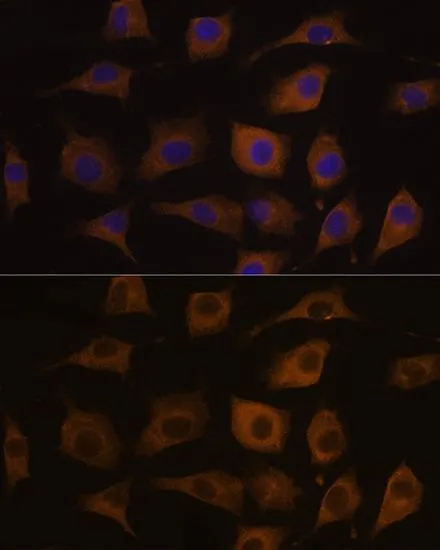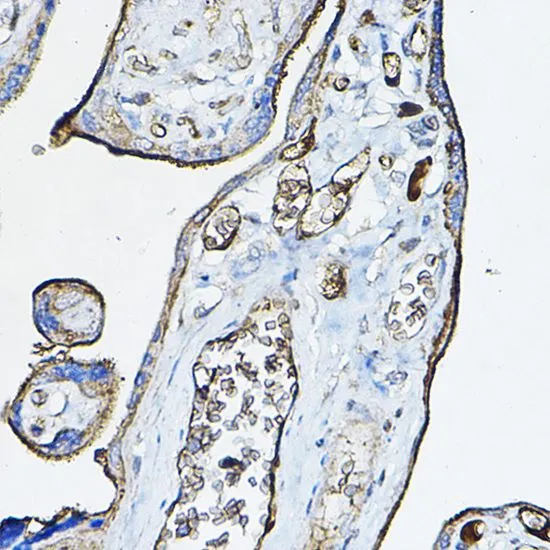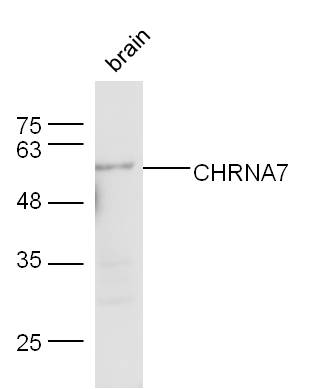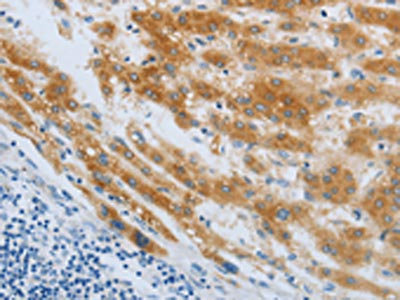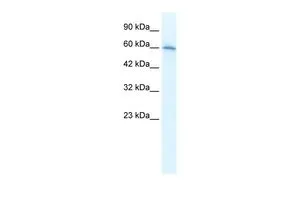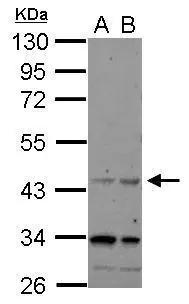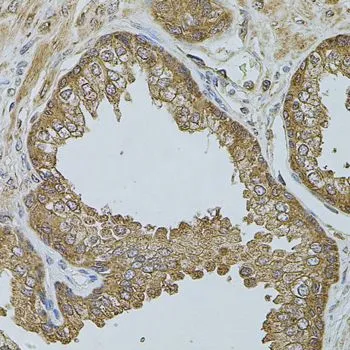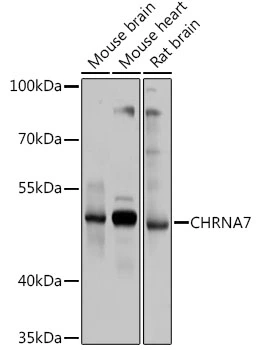
WB analysis of various sample lysates using GTX64511 AChR alpha 7 antibody. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25μg per lane
AChR alpha 7 antibody
GTX64511
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCHRNA7
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameAChR alpha 7 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. ICC/IF: 1:50 - 1:200. IHC-P: 1:50 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1139
- Target nameCHRNA7
- Target descriptioncholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 7 subunit
- Target synonymsCHRNA7-2, NACHRA7, nAChR7, neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-7, a7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, alpha 7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, alpha-7 nicotinic cholinergic receptor subunit, cholinergic receptor, nicotinic alpha 7, cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 7 (neuronal), cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha polypeptide 7, neuronal acetylcholine receptor protein, alpha-7 chain, nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-7
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP36544
- Protein NameNeuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-7
- Scientific DescriptionThe nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are members of a superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels that mediate fast signal transmission at synapses. The nAChRs are thought to be hetero-pentamers composed of homologous subunits. The proposed structure for each subunit is a conserved N-terminal extracellular domain followed by three conserved transmembrane domains, a variable cytoplasmic loop, a fourth conserved transmembrane domain, and a short C-terminal extracellular region. The protein encoded by this gene forms a homo-oligomeric channel, displays marked permeability to calcium ions and is a major component of brain nicotinic receptors that are blocked by, and highly sensitive to, alpha-bungarotoxin. Once this receptor binds acetylcholine, it undergoes an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. This gene is located in a region identified as a major susceptibility locus for juvenile myoclonic epilepsy and a chromosomal location involved in the genetic transmission of schizophrenia. An evolutionarily recent partial duplication event in this region results in a hybrid containing sequence from this gene and a novel FAM7A gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Lowered levels of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and elevated apoptosis in the hippocampus of brains from patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and db/db mice. Xu Y et al., 2020 Jul 23, Aging (Albany NY)Read this paper
- Expression levels of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in the brains of patients with Alzheimers disease and their effect on synaptic proteins in SH-SY5Y cells. Ren JM et al., 2020 Sep, Mol Med RepRead this paper
- Protections against toxicity in the brains of rat with chronic fluorosis and primary neurons exposed to fluoride by resveratrol involves nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Zeng XX et al., 2020 Jul, J Trace Elem Med BiolRead this paper