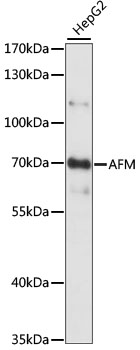
WB analysis of human cerebellum lysate using GTX88333 AFM antibody, Internal. Dilution : 0.3μg/ml Loading : 35μg protein in RIPA buffer
AFM antibody, Internal
GTX88333
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetAFM
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameAFM antibody, Internal
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.3-1microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.50 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID173
- Target nameAFM
- Target descriptionafamin
- Target synonymsALB2, ALBA, ALF, afamin, alpha-Alb, alpha-albumin, vitamin E binding protein
- HostGoat
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP43652
- Protein NameAfamin
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene is a member of the albumin gene family, which is comprised of four genes that localize to chromosome 4 in a tandem arrangement. These four genes encode structurally-related serum transport proteins that are known to be evolutionarily related. The protein encoded by this gene is regulated developmentally, expressed in the liver and secreted into the bloodstream. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
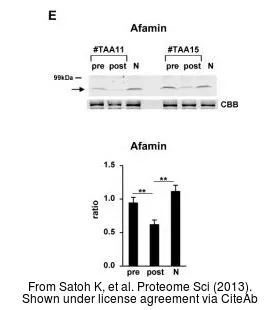
- Proteomic profiling for the identification of serum diagnostic biomarkers for abdominal and thoracic aortic aneurysms. Satoh K et al., 2013 Jun 27, Proteome SciRead this paper